Dashpivot article – Health and Safety Plan requirements
Health and Safety Plan Requirements
Health and Safety Plans are not the same across different industries depending on their application, focus, risks, and even regulatory requirements. In this article we will walk you through the various unique requirements what these plans need in your industry.

Table of Contents
Article Summary
- A construction Health and Safety Plan must be documented in a good standard format that provides a comprehensive detail of the procedures of the activity and a field to assess the hazards of the work procedures and environment.
- Unlike many other sectors, the construction, mining, and chemical industries are considered high-risk due to their greater number of hazards. Because of this, the health and safety plans of these industries have more unique requirements.
- It is important that these industries comply with the additional requirements to effectively provide appropriate control measures and procedures to eliminate all hazards found in their work environment.
Why are Health and Safety Plan Requirements essential?
Health and Safety Plan requirements are essential because high-risk industries like the construction, chemical, and manufacturing industries pose high-risk hazards, which cannot be addressed by generic safety plans. Requirements are needed to make sure that businesses turn their intentions into actions. These industries require more than simple plans to use in their workplaces because they require specific safety work measures. Focused health and safety plans are vital in these industries to effectively eliminate their high-risk hazards.
The Bureau of Labor Statistics reports that over 1069 people died in the construction industry in the United States in 2022. And according to the Herald Sun, the mining sector in Australia is responsible for around nine fatalities annually. Data from China also shows that 1,325 recorded deaths in the chemical industry were caused by 295 chemical accidents.
Unique and high-risk hazards can cause severe and irreversible fatalities, that's why regulatory bodies have mandated specific requirements in each industry to effectively control them, along with essential documents that come along with it. These standards serve as a guide and base on how businesses can draft their own unique and focused health and safety plans. Overtime, plans have become more tailored and accurate to eliminate unique hazards, providing safer and healthier workplaces.
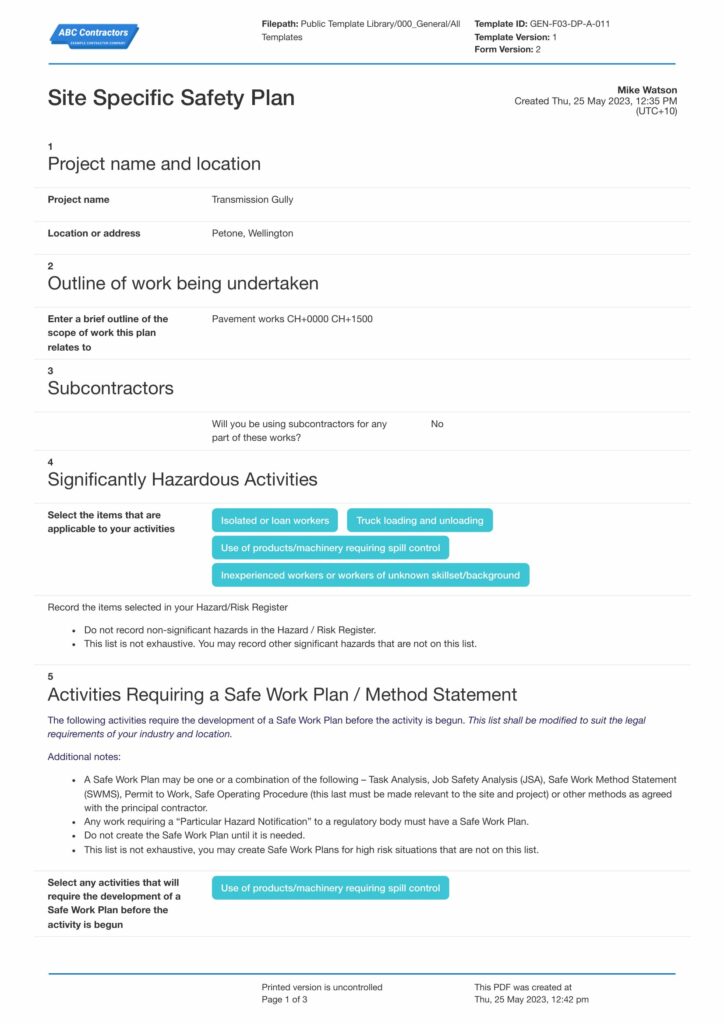
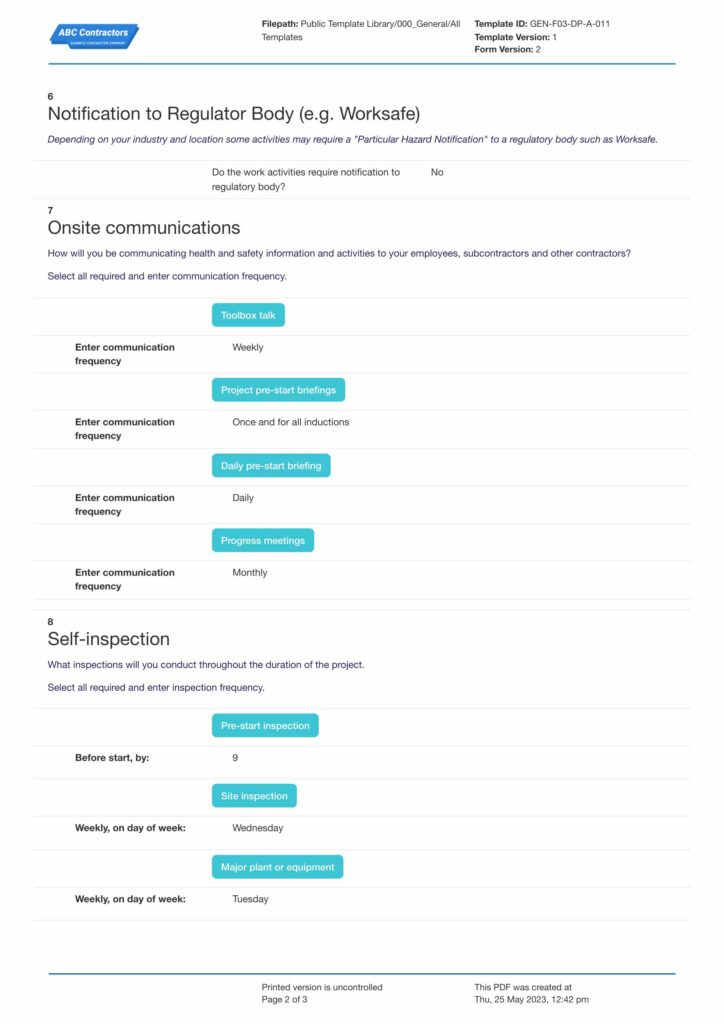
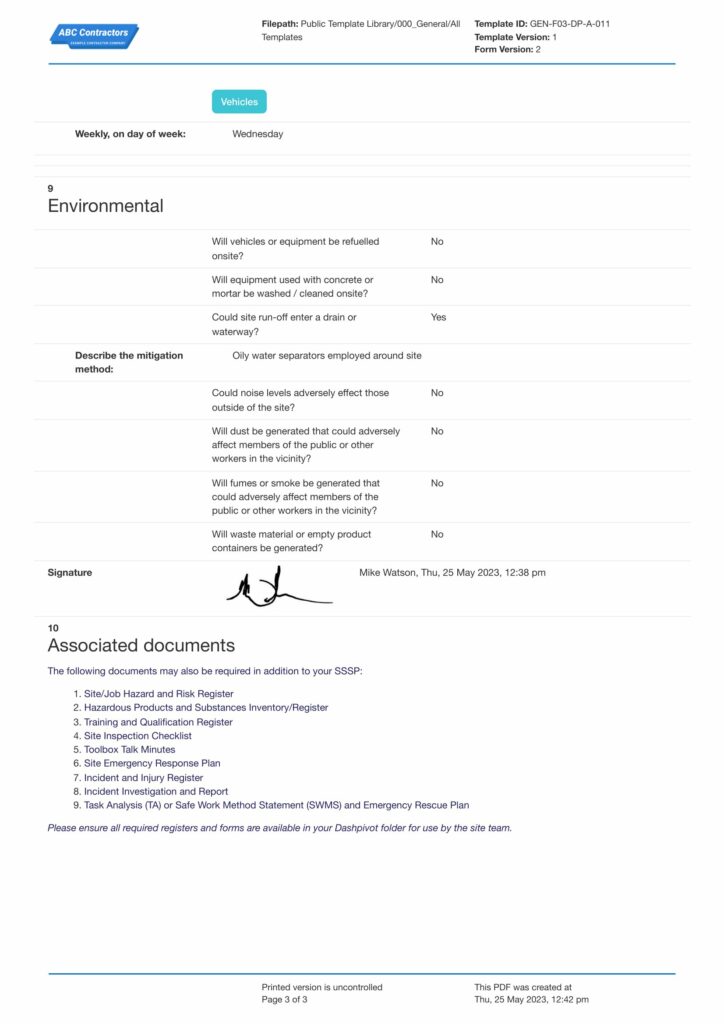
A quality example of a Construction Health and Safety Plan
Documenting a Health and Safety Plan is necessary to guide workers in practicing safe procedures and to effectively record assessments of the environment and work processes. Having a good standard format for the plan must be comprehensive in content to aid in identifying hazards easily and to give a clear work method statement for work procedures.
With different hazards across various high-risk industries, no Health and Safety Plan is ever the same. There may be core elements that remain consistent, but it should tailor to fit unique settings and surroundings. See this perfect, usable example below on how your Health and Safety Plan should generally look like. Incorporate existing or new elements that perfectly fits your business.

Use this Construction Health and Safety Plan for free
What are the required elements in a construction Health and Safety Plan?
Safe Work Method Statements
Unlike other industries, the construction industry has multiple high risk works like working at heights, hot works, demolition activities, and many more that make use of numerous heavy equipment for activities like excavation and trenching. High risk activities need activity-specific hazard assessments.
Traffic Management Plan
Construction sites pose a threat and hazard to pedestrians and vehicles passing by the site. That's why a traffic management plan should be included in your Health and Safety Plan if the worksite is nearby heavy streets. Plans for traffic management are necessary to guarantee the efficient and safe flow of both cars and pedestrians on building sites. These strategies reduce traffic disturbances, improve safety, and assist in controlling traffic flow.
Safety Integration of All Relevant Parties
On site, you have multiple people working together – employees, contractors, supervisors, managers, engineers, and even visitors. Having many people all in one place invites chaos due to different methods and practices. All relevant parties must agree on a program to provide a unified understanding of all related work procedures. This program must include defining the roles and responsibilities of all relevant parties and subcontractor prequalification, orientation, and oversight.
What should a mining Health and Safety Plan contain?
Geotechnical Risk Management
Mining poses unique geotechnical risks in its operation. Considering such risks, general control measures in the HASP would not suffice for these kinds of operations. The specific control measures for this industry must incorporate a mining risk register, ground stability plan, geotechnical monitoring systems, and mandatory ground supports. These controls provide slope stability, underground deformation, and awareness of land movements and seismic activities.
Ventilations Plans
In underground mining, ventilation plans are essential for ensuring safe and effective operations. Mining companies must design a sufficient mine ventilation system to enhance the underground air quality. In order to track the accumulation of toxic gases underground, monitoring systems must be incorporated into the ventilation design. Therefore, the ventilation system must be included as a requirement in the HASP for underground mines.
Explosive Safety Management
Explosives are naturally part of mining. However, this activity poses risks that could lead to serious injuries or even fatalities. Because of this, a specific program for explosive safety management is required. This program provides a detailed and documented procedure for handling, using, and storing explosives. Furthermore, the program should also detail specific instructions for magazine security protocols, misfire procedures, blasting area clearance, ignition timing, blasting alarms and awareness, and vibration monitoring.
Tailings Management Program
Mines usually produce waste called tailings. These wastes are contained in tailings ponds and usually contain heavy metals, radioactive materials, and toxic substances that could potentially harm affected communities and the environment. Because of this, these ponds require careful management. The HASP should include stability monitoring of tailings ponds and dams and an environmental risk management system.
Mine Emergency Response Plan
Preparing for mine emergencies is required in the HASP. The program should specifically address mine emergencies, such as protocols for handling cave-ins, underground fires, and explosions; mine flooding; search and rescue operations; worker tracking; and emergency communication. These emergency scenarios require more technical procedures, which is why the training of personnel to respond to such emergencies should also be included in the program.
What should be included in a chemical Health and Safety Plan?
Chemical Hazard Identification and Control (HazCom)
Unlike other hazard identification, HazComs require chemical companies to provide an inventory of chemicals called a chemical inventory. Furthermore, the target of a chemical risk assessment is to protect the health and safety of the general population, including consumers and others who handle chemicals. It entails determining the chemical's composition, the processes involved, the potential outcomes, the severity of the exposure, and the circumstances and procedures that may result in a chemical reaction that is more dangerous.
Process Safety Management
There are chemical companies that handle huge quantities or volumes of highly hazardous chemicals. For these types of companies, process safety management is required to be included in their HASP. This program lays out the process hazard analysis, inspection of the mechanical integrity of machinery used, specific operating procedures, and shutdown protocols.
Chemical Exposure and Monitoring Controls
Exposure to hazardous chemicals is the most prominent risk in this industry. Providing monitoring systems to detect leaks and releases is required in these industries. Furthermore, employees in these companies must undergo frequent medical checkups to constantly monitor their health. This program ensures that the employees are healthy and are not developing diseases.
Reactivity Hazard Programs
Chemical companies are required to conduct Hazard and Operability studies (HAZOP) as part of their health and safety plan. HAZOP is a methodical technique for spotting possible concerns and problems in complex systems. This systematic approach looks at both new designs and current operations to identify safety hazards and process inefficiencies. Providing this in the HASP continuously updates the needed control measures to make chemical plants hazard-free and efficient.
Spill and Release Response Plans
Chemical spills and releases are dangerous chemical plant emergencies. These situations could result in significant exposure to hazardous chemicals, reactions that may cause fires and explosions, and irreversible damage to soil and water, which can impact plant and animal life. Therefore, the creation of a specific emergency response program for chemical industries is necessary. The program should include a dedicated Hazard and Materials team (HAZMAT), and spill control measures like secondary containments, emergency neutralizing agents, and spill kits should be included and defined.
Smarter and better ways to make Health and Safety Plans
Filling out paper-based health and safety plan forms may be tiresome due to the several procedures involved, leading to multiple errors. Errors on essential documents that provide worker safety would undermine the entire purpose of creating the health and safety plan. Manual methods also take a really long time to create and submit, which postpone the implementation of solutions required to protect workers.
By using this Safety Plan App and this Health and Safety Reporting App to assist and manage your Health and Safety Plans, guarantee effective and compliant plans for your business. These tools are specifically designed for health and safety plans, making it simple and easier to stay on top of your regulatory compliance. Keep teams informed on any updates, request, and approvals with your safety documents. You could also include images and videos of your construction site's risks, dangers, and conditions to help your team understand what you're talking about in the health and safety plan. Get actionable data on on-site health and safety to provide you with insights on the status and effectiveness of your plans.
Summary of Health and Safety Plan Requirements
When it comes to the provision of a health and safety plan, various sectors of the economy have varying standards to meet. The high-risk industries present significant hazards, prompting the implementation of these differences in standards. It is necessary to provide extra measures or use different methods to properly manage and remove the hazards found in these industries. Because of this, businesses that are considered high-risk, such as construction, chemicals, and mining, are subject to extra requirements when it comes to developing their health and safety plans.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are health and safety plans required in all high-risk industries?
Yes - it is always required across all high-risk industries, but the structure and even the regulatory requirements vary by country, region, or industry.
How is technology changing how people process their health and safety programs?
Technology is transforming health and safety program management by replacing traditional paper-based systems and disconnected tools with digital solutions like Dashpivot. Teams can now streamline inspections, track incidents in real time, and ensure compliance through automated workflows and mobile accessibility. This leads to improved efficiency, more accurate reporting, and a stronger safety culture across worksites.
Does Sitemate offer other safety templates for construction, chemical, and mining safety?
Yes - Sitemate offers ready-to-use and editable construction templates, chemical-related templates like chemical risk assesment form, and mining-related templates like risk register template for mining that can also be edited for your workflow. Companies of all sizes in these industries are using these templates right now to streamline on accounting the hazards and risks associated and ensure the work environment is safe and compliant.
Related resources

Safe Work Procedure
Keep people following safe every day work procedures, with ease.

Site Specific Induction
Speed up your site induction process to keep people and projects moving forward quickly - and in an organised manner.

Weekly Safety Inspection Checklist
Get your weekly safety inspections done easier and faster, and then keep them all organised and easily searchable.