Dashpivot Article – How Often Should Power Tools be Inspected?
How Often Should Power Tools be Inspected?
In this article, we will be discussing the frequency of inspecting your power tools and how you should inspect your power tools.

What is a Power Tool?
Power tools are an alternative to hand tools that are powered by external sources of energy, like batteries, electricity, or engines. They are able to successfully carry out a broad variety of activities because of the power and accuracy that they give. These machines are able to do jobs in a much shorter length of time and with a significantly better level of efficiency as compared to hand tools used for the same purpose. The operations that are carried out in nearly every industry have been transformed as a consequence of the modern approach that power tools have brought to the table courtesy of their introduction.
Why should Power Tools be inspected?
The fact that these instruments appear to be incredible does not change the reality that they are not without hazards. These risks have the ability to inflict damage not only to those who use them but also to those who are in close proximity to them. Power tools, despite the fact that they are beneficial, have the potential to be counterproductive if the right safety precautions are not taken and correctly executed when using them. This is because power tools have the ability to do unnecessary harm. Establishing specific safety guidelines for the usage of power tools is something that organisations and enterprises ought to do in order to achieve the goal of eliminating these dangers. Regarding the purpose of assisting you in getting familiar with some of these safety measures, we will offer you some safety advice regarding power tools. To know more about safety tips, read more at power tools safety tips.
How Should Power Tools be Inspected?
It is necessary that organisations and companies perform a full inspection on power tools in order to retain their usable life and maintain a safe and healthy working environment. Now that we have established how power tools might be harmful, it is imperative that these items be inspected, and extensive inspections should be conducted. For the purpose of the current section of the article, we will be examining the many methods of inspection that can be performed on power tools.
Risk Assessments
The main emphasis of this type of inspection will be the risks associated with power tool use. The steps and procedure for utilising the power tools will be examined, and the risks associated with each step are noted and ranked according to their potential impact and frequency. This type of assessment will give businesses and organisations adequate information to acquire the right safety measures to get rid of and lessen these risks. Additionally, this will ensure adherence to legal requirements, enhancing a business's safety and health reputation and preventing fines for non-compliance.
Having said that, it is crucial to do thorough risk assessments in order to protect assets and personnel, and the most effective method of doing so is digitally using the risk assessment software.
Visual Inspections
The main emphasis of these comprehensive inspections is the condition of the equipment. The essential components are often mentioned on its checklist, and every component is closely inspected for defects and problems. It will then be scheduled for maintenance repair if any parts are problematic. A power tool's lifespan is significantly increased, and its optimal condition is maintained using this sort of procedure. Since your tools and their components are guaranteed to be in a condition that allows them to operate correctly, this also removes the chance of downtime. It would also guarantee safety when using power tools, which is another impact. Power tools that are properly maintained are less prone to breaking down. Malfunctioning can result in hazardous circumstances, harm workers, and destroy property.
Functionality Tests
The majority of power tools operate precisely. Because of this, power tools can only be used under specified conditions. A functionality test must be performed to see whether your power tools continue to function within these parameters. A functionality test's goal is to confirm that every part of the system functions as intended under controlled circumstances. If the power tools are placed in a certain state, doing this will assist in identifying faults and issues. Additionally, this will guarantee that the power tools are operating at their best and can function effectively in these particular circumstances. This will also shed light on the potential risks associated with using such a power tool. The risks involved can then be eliminated by adding these hazards to the risk assessment and providing the appropriate measure.
Lubrication Inspection
Power tools are heavily reliant on lubrication. Power tools are often made up of components like gears, bearings, and rotating joints that come into constant contact with one another. Friction is created when there is continuous contact at high speeds, heating the parts that contact. Lubrication is required to significantly decrease friction between these contacting elements. Lubrication can extend a power tool's life, minimise wear, and ensure smooth operation. Naturally, though, this will only occur if the right lubricant is applied carefully and in accordance with the manufacturer's advice. A lubrication inspection is necessary to further guarantee that your power tools are routinely and appropriately lubricated.
Storage Conditions
Power tools must be stored properly to maintain their quality and protect them from environmental elements that might harm them. Dryness and cleanliness are two essential qualities for a power tool storage unit. A power tool's metallic components may oxidise in high moisture environments, causing rust and corrosion. Once the power tool is switched off, dust can enter its cracks and settle on its revolving parts, causing harm to the tool when turned on. Additionally, it is strongly advised that power tools be kept in a temperature-controlled space. Plastic shields and casings, which are crucial for ensuring safety when using the power tool, might melt or get damaged in extremely hot or cold environments. All things considered, making sure your power tools are stored properly contributes to their overall health and dependability.
Creating your Power Tool Checklist
You are required to create a detailed checklist of all of the necessary components that can be found on your power tool in order to ensure that your employees and assets remain safe while also ensuring that your power tool continues to operate well. You may do this by utilising a digital inspection checklist, which will make things simpler for you. Utilising digital checklists will ensure that your inspection forms are uniform, hence reducing the amount of variation that exists between the various inspectors' work. Now that you have this, you will have a standard form that includes all of the essential components. In addition, the utilisation of a digital checklist contributes to an even greater enhancement of efficiency while carrying out inspections. The inspection procedure is sped up and the likelihood of overlooking significant particulars is reduced when there is a clear guide that outlines what should be inspected.
Power Tools Inspection Documentation
One of the questions which quickly follows how often should power tools be inspected is "how do we properly inspect power tools?".
The best way to handle these inspections is by following a basic checklist, like the below, ensuring you are documenting your inspections for asset management and safety purposes.
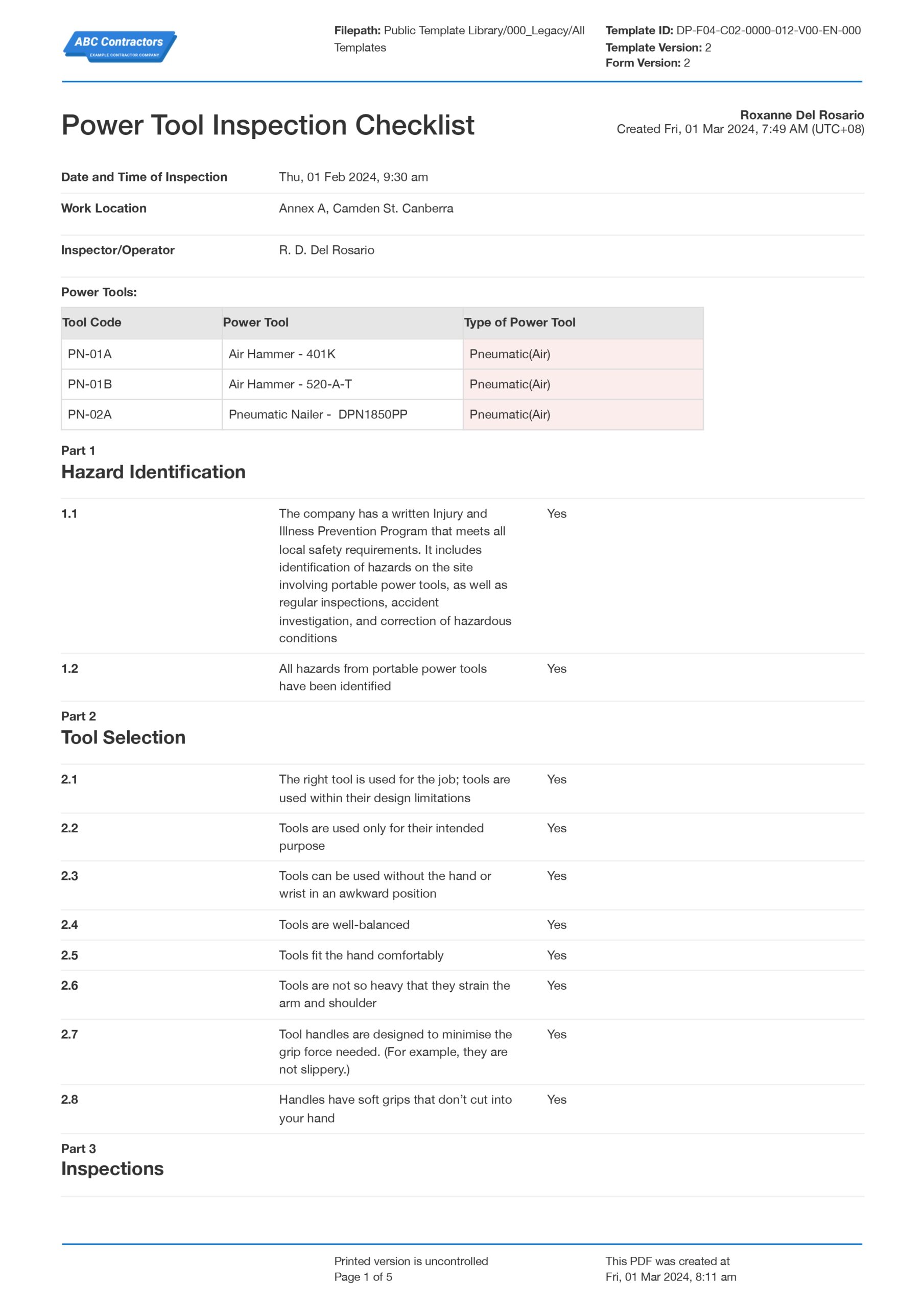
Use this free Power Tool Inspection Checklist for free
How Often Should Power Tools Be Inspected?
After talking about how power tools should be inspected, we'll talk about how often they should be inspected. There are several recommendations for how frequently to check these effective instruments, and we will share these recommended frequencies with you in this section of the article.
Before Every Use
At this frequency, the primary objective is to determine whether or not the equipment is safe to use, whether or not it is the appropriate equipment for the task at hand, and whether or not it is functioning at its highest possible level. Due to the fact that the power tool will be operating in an effective and secure manner, this will guarantee that the activity will go without any hindrances while it is being carried out.
After Every Use
After utilising the power tools for the activity, it is essential to do a thorough inspection of them. In this way, any potential damage or issues with the power tool may be identified and addressed. Having this information allows for the procedures to be reexamined in order to be improved and for those that result in the power tool being damaged to be altered. Additionally, by performing these inspections at this regularity, you will always be able to ensure that the power tools are stored in the appropriate location and will prevent them from being kept in regions where the conditions are damaging.
Weekly Inspection
In comparison to the two frequencies that were discussed earlier, these are planned inspections that do a more comprehensive examination. The purpose of this is to examine all of the components of these instruments to see whether or not there are any damages and whether or not there is sufficient lubrication to the moving parts. In addition, tests are carried out to determine whether or not the instruments continue to perform in their entirety while they are used at their particular settings. Incorporating this frequency into your inspection schedule will undoubtedly result in a significant extension of the life expected from the power tools.
Scheduled Extensive Inspections
The power tools that have been discovered to be damaged are subject to these examination frequencies. It is possible to draw parallels between these checks and the way in which we go through medical exams. For the purpose of determining the underlying source of the issue, a series of examinations is carried out. Following the identification of the issue, the necessary maintenance is then arranged in order to remedy the issue.
A Smart Report for Your Inspections
For inspections to become useful, a comprehensive report must be created to generate data and trends to provide solutions and predict future outcomes of your power tools. But uploading your inspections manually might be a hassle. When doing this the traditional way, you have to encode every line of your inspection to your office computer, which is prone to errors and repetition of data. These might alter results, which are crucial for future maintenance schedules. Furthermore, when making your reports, you have to open another app to create visuals for your presentation, especially with the trends, so you have to import your data from the written report to your presentations. This is another room for possible errors when making your presentations.
However, there is now a smart way to create your inspection reports by using the Dashpivot Inspection Report App. Instead of using Word, PDF, or other formats, create your inspection reports in an intelligent digital format that makes them easier to use and maintain. Make as many different inspection templates as you like, including ones for environmental, quality, and safety reports. You have the option to choose from our extensive collection of free inspection reports or create your own structure and report contents from the beginning. Furthermore, you can immediately generate reports even though you're still in the field. Using any computer, tablet, or smartphone, access, update, and finish inspection reports from the office or the field. With powerful features like offline mode, digital signatures, autosave, and immediate share, the inspection report app was made to be simple to use from any location, making reporting simpler than ever. To ensure that everyone has access to the precise inspection reports they want, you may even assign particular reports to particular teams and projects. These remove all the possibilities of committing errors in making your reports.
All these and more in the Dashpivot Inspection Report App; to learn more about it, see more at Dashpivot inspection report app.

Safe work method statement for power tools
Power tools pose a constant hazard and risk to many workers. Ensure everyone is using and managing power tools properly with a good SWMS.

Extension Cord Safety Toolbox Talk
Avoid incidents involving extension cords, tripping and electrical hazards with this Toolbox Talk template.

Cable Inspection Checklist
Keep all of your power and electrical cables in good and safe 'hands' by properly inspecting your cables with this checklist.