Article Page – How Much Exposure to Crystalline Silica is Dangerous?
How Much Exposure to Crystalline Silica is Dangerous?
In this article, we'll discuss what and how respirable crystalline silica is formed, and how prolonged exposure and inhalation can be dangerous to field workers' health and well-being – along with free tools and resources to control exposure and develop a safety-first mindset workplace.

Table of Contents
Article Summary
- Protect workers from respirable crystalline silica, the fine, airborne, dust-like substance that can cause severe, irreparable damage to your lungs when inhaled repeatedly or in high concentrations by using a Silica Dust Exposure Control Plan.
- OSHA has set two important exposure limit levels: the Action Level (AL) and the Permissible Exposure Limit (PEL).
- Engineering exposure controls and other safe work practices are outlined by OSHA in their Silica Dust Fact Sheets FS 3682 and FS 3681.
- Going digital helps you and your team stay on top of any risk assessment procedure before or as soon as risks are identified before operations.
Why Should Silica Dust be Included in Risk Assessment & Safety Plans?
Silica Dust, in the form of respirable crystalline silica, poses serious threats to the health and well-being of your team and to others who inhale the substance in high quantities. When left unprotected, workers are highly likely to develop severe, and oftentimes incurable, diseases.
The Hawk's Nest Tunnel disaster in the 1930s is considered one of the worst industrial workplace tragedies in U.S. history. Over 700 workers, mostly African American, died from acute silicosis after drilling through silica-rich rock without proper protection.
Due to the nature of work required in industries like construction, manufacturing, mining or rock quarrying, and even cosmetics, exposure to silica dust is oftentimes unavoidable. This makes planning and exposure control management against silica dust in these industries critical and highly relevant.
In the modern built world, several safety regulators like OSHA have set strict standards to help mitigate risks when dealing with silica dust, like regulations on risk assessment, safe work practices, engineering solutions, and exposure control plans.
How Should You Format a Written Exposure Control Plan for Silica Dust?
As required by OSHA, a proper written exposure control plan for silica dust should include the following information: a description of the tasks that produce silica dust, engineering controls and practices, housekeeping measures, procedures on exposed area restriction, and the designation of a competent person to implement these plans.
Depending on the task required, OSHA has provided recommendations on how employers can comply with their standards. After making sure all regulations have been complied with, you will also need to ensure your written exposure control plan can be communicated properly with your workers by providing copies of the plan to them as soon as possible after request.
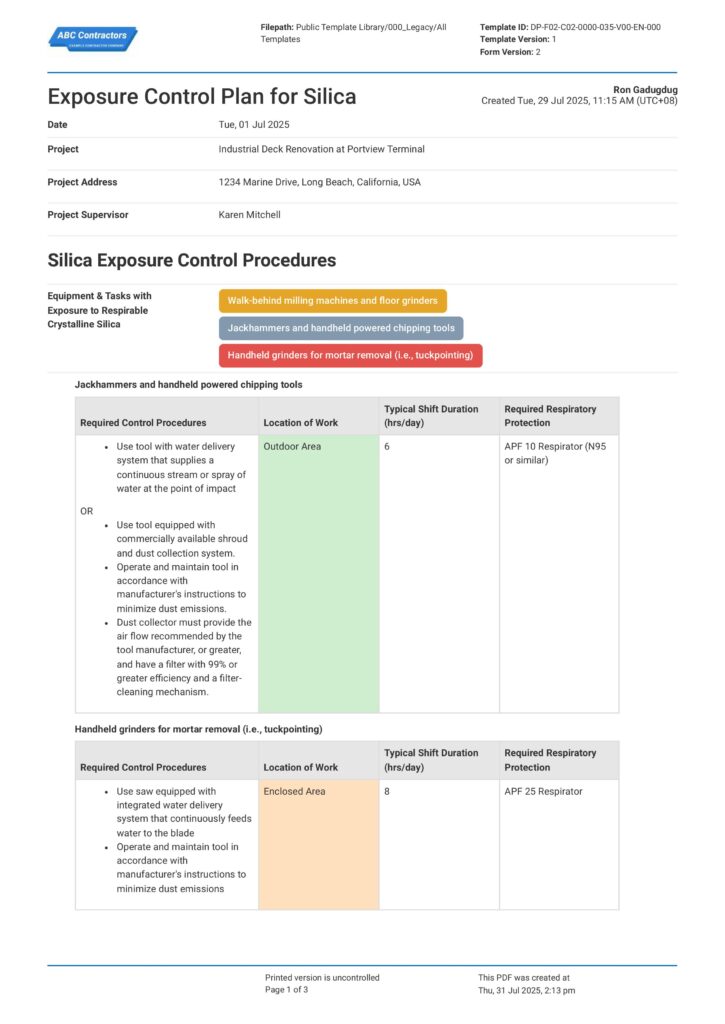
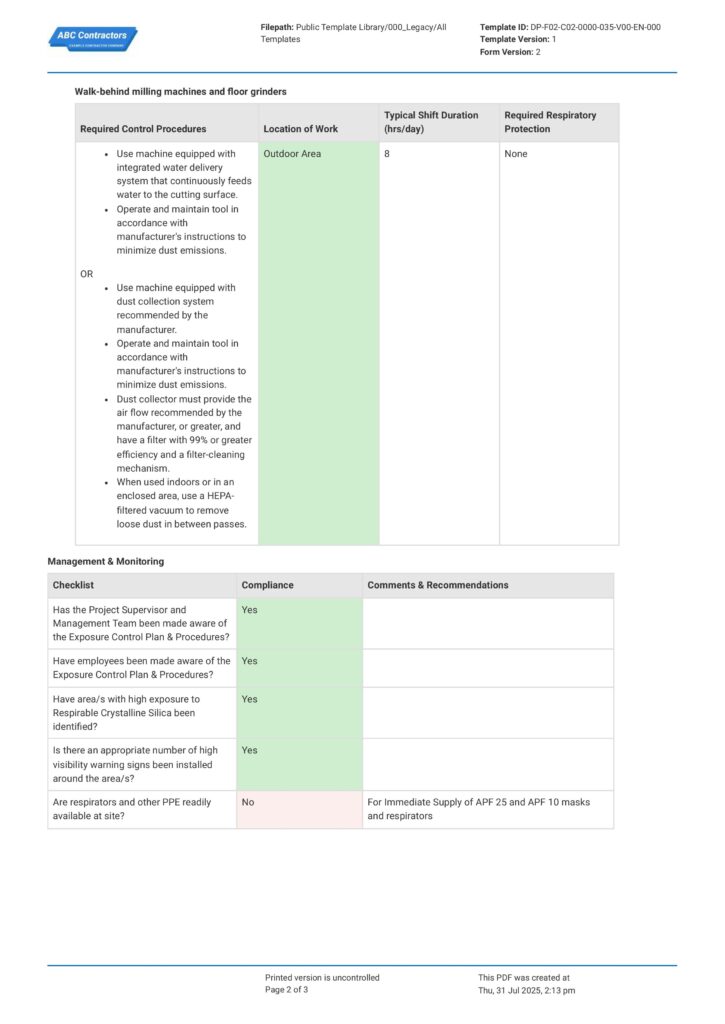
Wondering how to structure your written control plan to comply with all of OSHA’s regulations? Preview the Exposure Control Plan for Silica Dust below for free.
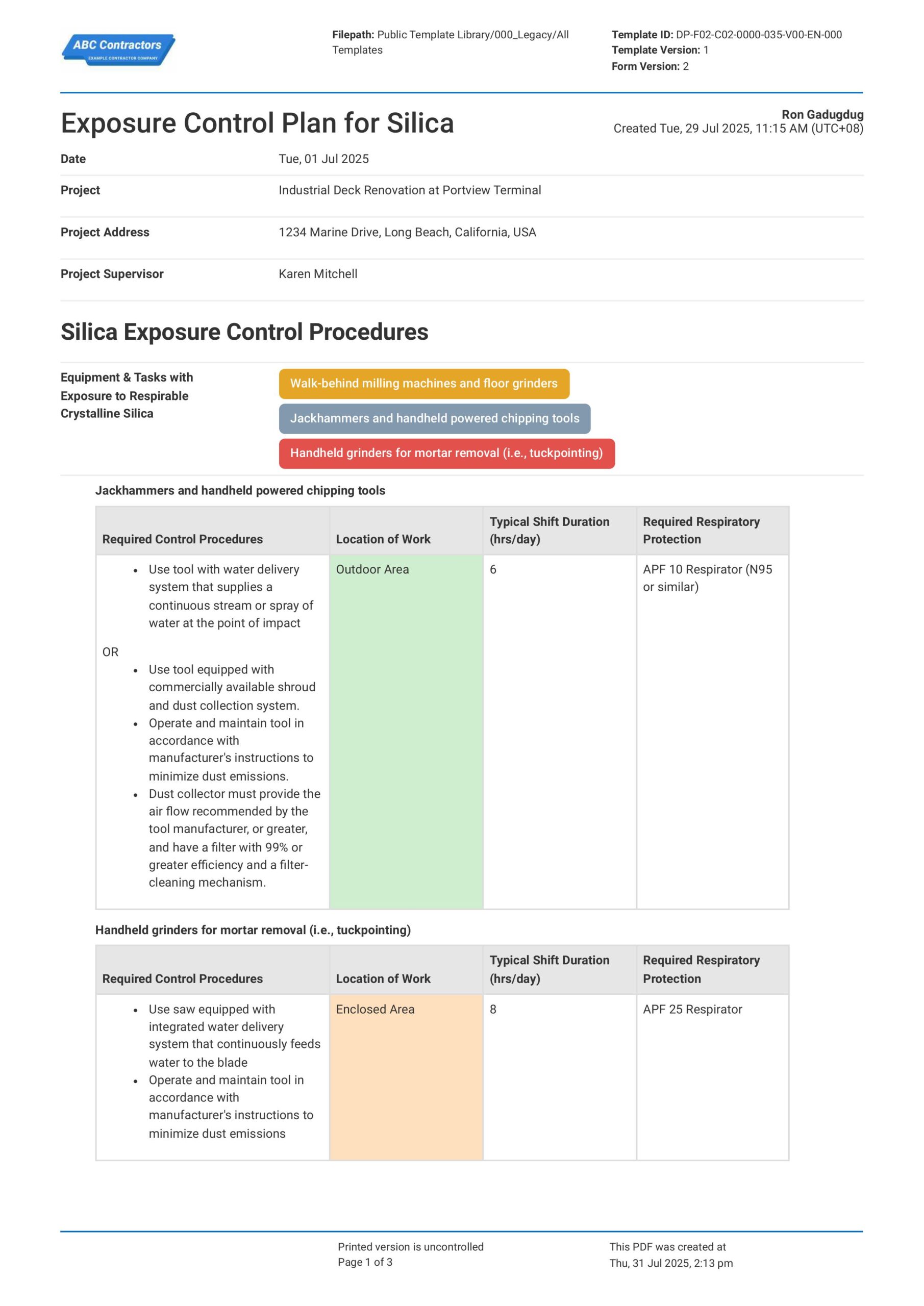
Use this Exposure Control for Silica Dust for free
What are the OSHA Crystalline Silica Exposure Limits?
OSHA has identified two Silica Dust exposure limits, of which employers are required to implement varying levels of exposure control measures:
- Action Level (AL) is set at a concentration of respirable airborne respirable crystalline silica of 25 μg/m3, calculated as an 8-hour TWA. This refers to the minimum level where exposure is monitored and protective measures must be implemented, such as wearing of PPE, etc.
- Permissible Exposure Level (PEL) is set at a concentration of respirable airborne respirable crystalline silica of 50 μg/m3, calculated as an 8-hour TWA. This refers to the maximum level of exposure allowed by OSHA. Strict compliance to the control methods listed in Table 1 of 29 CFR 1926.1153. Employees who are exposed to above PEL for 30 days or more are further required to undergo regular medical surveillance.
These limits were set based on extensive scientific research, epidemiological study, and risk assessment. At the PEL of 50 μg/m3, it was determined that while health risks from exposure to silica dust significantly increased, it also became technologically and economically feasible to provide the adequate personal protection equipment to help mitigate these risks.
Conducting Silica Exposure Monitoring
OSHA requires that employers conduct Silica Exposure Monitoring when their workers are reasonably expected to be exposed to at least the Action Level (AL) of respirable airborne respirable crystalline silica of 25 μg/m3, calculated as an 8-hour TWA. Monitoring is done primarily via testing and examination of personal breathing zone air samples.
As set by OSHA, employers are required to conduct two kinds of monitoring:
- Initial Monitoring - Required to determine the exposure level of workers performing a certain task. Can be forgoed if the employer can present existing monitoring data that show exposure levels below the AL.
- Periodic Monitoring - Employers are required to conduct exposure monitoring every 6 months when exposure levels are above AL but below PEL, and every 3 months when exposure levels above PEL.
If two consecutive monitoring results show exposure levels that do not exceed the AL, then further monitoring can be discontinued. Further, employers are required to share and communicate the monitoring test results with the affected employees 15 days after receiving them.
The OSHA Crystalline Silica Fact Sheets
To better communicate regulatory standards regarding the risk of exposure to respirable crystalline silica, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) released two Fact Sheets for employers to review:
- Fact Sheet FS 3682 (2018, for General Industry and Maritime industry)
- Fact Sheet FS 3681 (2017, for Construction industry)
Both these fact sheets act as summaries of OSHA regulations 29 CFR 1926.1153 (for construction) and 29 CFR 1910.1053 (for general industry and maritime). The fact sheets contain information on employer obligations and responsibilities, silica dust exposure limits, engineering control methods, safe workplace practices, exposure monitoring requirements, and regulations regarding housekeeping practices, medical surveillance, and record keeping.
Respirable Crystalline Silica Exposure: Health Hazard Information
Respirable Crystalline Silica is produced when materials like stone, concrete, or brick are cut, drilled, or fractured. When inhaled in large amounts, silica dust causes the scarring of lung tissue, also known as fibrosis. Oftentimes, it has shown to develop into severe and incurable diseases such as silicosis, lung cancer, COPD, and kidney disease.
Respond Quickly to Workplace Risks with Digital Risk Assessments
Due to the dynamic nature of site work, managers and supervisors oftentimes find themselves having to quickly react to the developments at the workplace. Having to deal with writing of risk assessment reports, taking and attaching photos, acquiring the necessary sign-offs each time a task needs to be performed can prove to be jarring to a team who is unprepared - not to mention the mountain of paperwork that needs to be archived afterward.
Fortunately, we live in a time when tech solutions can help alleviate some of these work loads. By going digital, you can use this Risk Assessment App on your phone, take down live notes, attach photos as soon as you take them, then save the form so you can access the form later on another device like your office computer for final edits.
With this Risk Assessment Software for Industrial Companies, you can easily create those assessment forms, attach any supporting documentation, gather the necessary sign-offs via e-signature, and quickly share the assessment with any concerned party.
For specific sites, get your assessments done quickly with this Personal Risk Assessment App and this PPE Hazard Assessment App so your team can move on with the real work. For more environmentally-conscious assessments, an Environmental Risk Assessment is the best tool to use.
Summary of Exposure to Crystalline Silica
Respirable Crystalline Silica can be hazardous when inhaled in large amounts or over an extended period of time. To set standard exposure control limits across industries, OSHA has formalized two limits: the Action Limit (AL) and the Permissible Exposure Limit (PEL). OSHA’s regulations can be reviewed in their Fact Sheets FS 3682 and FS 3681.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does OSHA require an Exposure Control Plan when dealing with Silica Dust in the construction, maritime, or general industry?
Yes - OSHA explicitly requires employers to create, maintain, and implement a written exposure control plan for silica dust. This control plan would include the company’s control measures on how to mitigate occupational and health risks when workers are exposed to silica dust.
How do digital tools play a role in improving modern-day exposure control measures?
Digital tools help speed up the work process for the modern-day engineer and act as their support. More and more companies are moving away from paper-forms and legacy software to perform repeated tasks like reports, assessments, and checklists. Digital tools like Dashpivot now allow you to create a standard form template, take that template wherever work is needed, create that report on-the-go, and safely store the report for future use online.
Does Sitemate offer templates for Silica Dust Exposure Control?
Yes, Sitemate offers ready-to-use templates for all your Exposure Control and Risk assessment needs - Silica Dust or otherwise. Fill out the templates on your phone and bring them anywhere work is needed - no spreadsheets required.
Related resources

Silica Dust Risk Assessment
Streamline the risk assessment process for dealing with operations that result into workers being exposed to silica dust.

Silica Dust Toolbox Talk
Capture and record toolbox talks prior to work operations and remind workers to wear proper protective equipment to avoid silica dust inhalation.

Site-Specific Risk Assessment
Automate the risk assessment process for any site-specific type of work operations or site – stay flexible and use efficient digital tools.