Dashpivot article – Occupational Health and Safety Plan
Occupational Health and Safety Plan
Read more about what an Occupational Health and Safety Plan is, how it's a key safety compliance document to make sure workers are safe and healthy, and how you can align it with your safety programs.

Table of Contents
Article Summary
- An Occupational Health and Safety Plan (OHSP) is the master document that outlines the safety policies of a company, their methods of hazard identification and risk assessment, emergency procedures related to the project/industry, roles and responsibilities, training records, reporting system, and many more. It's required as proof that companies in high risk industries are making sure they're managing risk and safety policies religiously.
- An OHSP is a live document, meaning as soon as there are significant changes in the work site or project, it should be regularly updated too. It is designed to be adaptable and flexible.
- You can demonstrate how dedicated and committed you are as a company towards safety by having a OHSP. Not only are you able to project your workers from preventable harm, you're also able to build trust with clients.
Why is an Occupational Health and Safety Plan (OHSP) important for safety compliance?
An Occupational Health and Safety Plan (OHSP) is important for safety compliance because it makes sure that businesses, companies, and employers are meeting at least, or better all, the regulatory requirements that manage the health and safety risks in the workplace.
An OHSP gives guidance on how to properly structure the entire framework of the necessary contents that reduces the instances of incidents, accidents, fatalities, etc. It’s not just about ticking boxes – in fact, you’re being guided on how to align with the industry standards. It provides the best practice to outline your hazard identification methods, risk assessment and investigations, and other safety-concerned procedures and protocols.
Agencies, like the International Labour Organization (ILO), don’t mandate an Occupational Health and Safety Plan (OHSP). This agency, like many others, creates the guidelines and best recommendations for regions and countries to follow. Despite not being mandated under ILO, OHSP still exists as a standard practice because ILO promotes the principles, structure, and how it can assist in making sure regions follow through. That’s the reason why regulators like OSHA, WorkSafe NZ, Safe Work Australia, etc. implement the guidelines of ILO through OHSPs; although some might not use the term “OHSP” specifically.
Even if it is or is not mandated, many clients and customers nowadays require an OHSP as proof anyway to see that businesses and companies especially in high-risk industries like construction, infrastructure, energy, mining, etc., risks are managed, and they’re promoting a culture of safety in the workplace and sites.
Tailor and format your OHSP across different worksites
A dynamic and live document like an Occupational Health and Safety Plan needs regular updating and adjusting depending on the change of environment, newly-discovered risks, and many more. That means, its structure needs to be flexible and easily editable. Aside from that, it’s not even a one-size-fits-it-all type of document. It actually varies depending on what industry you are in, or the type of project you’re working on. That’s why one company shouldn’t be using the same format and content for two projects. It’s key to tailor and format your OHSP using a proper structure and even site-ready like this OHSP example below.
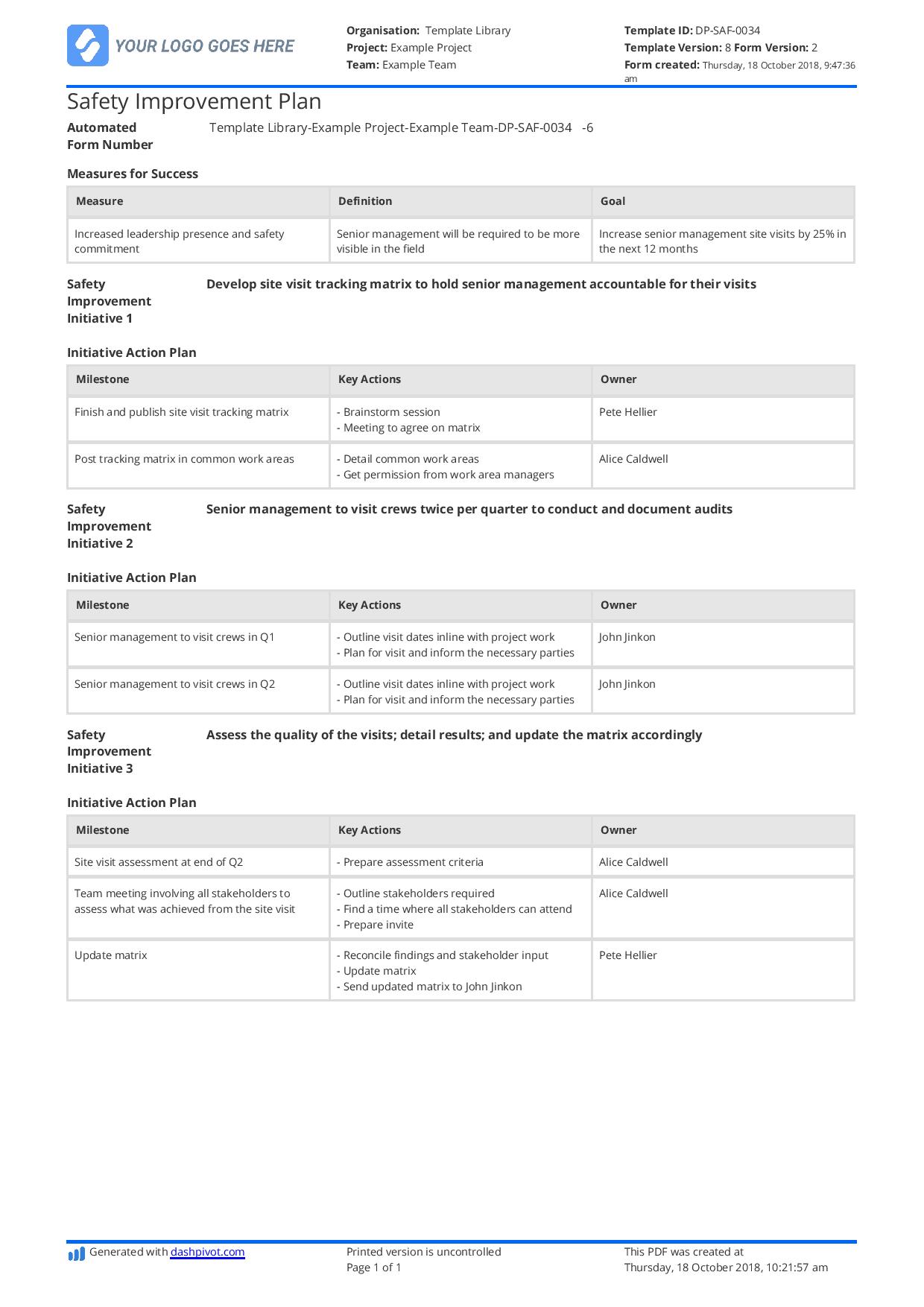
Use this Occupational Health and Safety Plan for free
How to use an OHSP as the foundation of all safety programs?
An Occupational and Health Safety Plan is best described as a master plan that covers the entire company/operations. It’s both comprehensive and detailed, that it addresses the main aspects in a workplace – like the company policies, hazard identification, risk assessment, workforce roles and responsibilities, emergency plans and procedures, training, compliance, etc. It is different compared to other safety and health related documents, like a Job Safety Analysis (JSA), Task Hazard Analysis (THA), or Emergency Action Plan (EAP) that are limited in scope.
If you’re confused whether you’re actually writing an OHSP, the naming doesn’t matter – for as long as you cover the following core elements aligned with the ILO OSH Guidelines and ISO 45001:
- A clear policy statement of the safety and health goals of the company and how the management can ensure they’ll stay aligned with them
- The roles of each key persons/personnel and their responsibilities in maintaining the safety protocols and procedures in the workplace
- JHA/THA or a section for hazard identification, risk assessment, and control measures
- Emergency response plan in case of emergencies (all kinds of emergencies related to the industry or hazards present)
- List and proof of training/certification/competency of the workers/personnel
- How workers can process for incidents, near misses, investigations, any kind of reporting related to incidents.
- Monitoring the site and the plan itself as a live document (revisions, changes, lessons, reviews, etc.)
Regulatory bodies may require to use the exact naming as “Occupational Health and Safety Plan” due to: (1) regulatory compliance, where using the wrong term would confuse the regulatory body; (2) contract; (3) strict clients, regulators, or inspectors who are strict with the terms, and; (4) just overall preference and local terms.
Read more about what the ILO says: How can occupational safety and health be managed?.
How does an OHSP differ from other health and safety-related documents?
A JSA, THA, and EAP are not health and safety plans on their own, but they fully support or are actually included in an Occupational Health and Safety Plan.
See their respective articles about examples/samples to fully understand the differences: JSA examples: Use these job safety analysis examples, Task Hazard Analysis Example, and OSHA Emergency Action Plan Sample.
Those task/site-specific documents mentioned above can be part of an OHSP, but it’s also important to note that countries may refer to OHSP differently depending on what’s commonly used in the region. Due to local naming, what’s famous, or what clients prefer, it might be named differently.
Aligning Your OHSP with other workplace safety programs
Workplace safety programs can be the very core principles you have within your Occupational Health and Safety Plan. Just because it seems redundant doesn’t mean it’s ineffective. In fact, in this case, all the more you highlight safety programs, the more likely the safety efforts stay consistent. Your employees are more engaging, you build this culture and mindset of safety, the workplace is safer, and it’s easier to comply with audits. Similar with the core elements in an OHSP, these are some workplace programs you can align with it:
- Regular safety training programs, drills, equipment handling, onboarding, etc.
- Conducting a strict and thorough flow of your risk assessment and hazard reporting system
- Develop a standard procedure for incident and near miss reportings
- Conduct proper inductions, permits to work, and monitoring with contractors and subcontractors, making sure that they follow the procedures as outlined in your OHSP
Digital tools to manage Occupational Health and Safety Plans and safety programs
Making sure that your workplace is safe shouldn’t even be bothersome, but with how demanding and highly dangerous high-risk industries can be, there are so many health and safety administrative works that need to be done. Aside from them being time-consuming, they could also be fragmented. Papers can’t physically help on the spot when everyone’s safety is at risk.
Yes, the Occupational Health and Safety Plans that companies draft prior to starting projects are extremely helpful, but it needs to be extremely detailed and thorough. Not to mention, sometimes it could be hard to actually implement the contents and safety programs involved. Furthermore, we’ve already established earlier in this article that OHSPs are living documents – so they need constant attention.
Digital tools make managing, implementing, and updating your OHSPs and other safety documents and programs easy and quick. By using these apps like a health and safety reporting app, safety planning app, and site safety app, you can put everything in one place, track all your health and safety documents, and keep everyone updated with the processes in real time.
With workplace safety programs ideally aligned to your Occupational Health and Safety Plan, you can include this training and qualification records app to record the certificates and training of your workers, conduct risk assessment easily using a risk assessment software, use tools to log safety incidents like this smart incident report software and near miss reporting app, and make sure that your contractors understand the safety protocols on site with proper approvals using a site induction app and a permit to work app and software.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is an Occupational Health and Safety Plan required for all high-risk indsutries?
Agencies like the International Labour Organization (ILO) have set guidelines and recommendations, which various local regulatory bodies use as basis for their regulations and standards. An OHSP fully aligns with the principles and supports the purpose of keeping workplaces a safe and healthy environment to work in. Additionally, clients require OHSPs to make sure that companies adhere to the local safety regulations. An OHSP may be named differently across regions but the core remains the same.
How is technology changing how people do Occupational Health and Safety Plan and other safety programs?
Technology is easily transforming how businesses do health and safety planning by making sure OHSPs and other live safety documents stay effective and relevant by using digital solutions like Dashpivot. Teams can easily review and update documents that align with the environmental changes, keep track of documents live, share to stakeholders and other team members, and keep all documents safely stored in the database. This leads to better data for analytics, a much safer environment, and fully aware and accountable workers.
Does Sitemate offer templates for Occupational Health and Safety Plan and other safety documents?
Yes - Sitemate offers a variety of ready-to-use and editable safety forms and templates that can also be incorporated into your safety policies and safety programs. Companies of all sizes in every high-risk industry, even low-risk, are using these templates right now to streamline their safety procedures. .
Related resources

Safe Work Procedure
Keep people following safe every day work procedures, with ease.

Site Specific Induction
Speed up your site induction process to keep people and projects moving forward quickly - and in an organised manner.

Weekly Safety Inspection Checklist
Get your weekly safety inspections done easier and faster, and then keep them all organised and easily searchable.