Article Page – Building Safety Act Explained
Building Safety Act Explained
Explore this article about the UK Building Safety Act 2022 explained to understand the measures taken to prevent another Grenfell Tower incident. We will also provide free guides and resources to the format of a Compliance Register to assist you in managing the requirements of this act.

Table of Contents
Article Summary
- The UK government made the Building Safety Act 2022 to make sure that residents occupying higher-risk buildings are protected. The UK government took this action in response to the tragic Grenfell Tower incident, which resulted in multiple fatalities.
- The six sections of the Building Safety Act cover the following topics: the legislative basis of the act, the duties of the BSR, the 1984 Building Act amendments, how to manage higher-risk buildings safely, providing transparency for tenants, and legal punishment for non-compliance.
- Other laws are crucial for giving residents continuous protection in addition to the Building Safety Act. These regulations must be taken into account in order for a building to have a functional and efficient building safety system in addition to being legally compliant.
What is the importance of the Building Safety Act?
The Building Safety Act of 2022 is important as it was established to be a countermeasure to prevent the Grenfell Tower incident from happening again. The tragedy claimed 72 lives, including people who later died in the hospital. This incident was considered one of the deadliest fires in the UK. Because of this, the UK government made new regulations with regard to occupied buildings, leading to the creation of the Building Safety Act 2022.
Despite the Act's focus on occupied buildings, some of its provisions also apply to buildings under construction. The Act imposes the implementation of safety checkpoints (gateway points) during the planning, design, and construction phases to assess whether the building meets all necessary safety requirements.
Having these UK building safety regulations implemented places accountability on the building management to ensure that residents and occupants of the building are always protected from harm. Penalties may result from non-compliance with this act. This includes fines, a potential suspension of all businesses operating within the building, and criminal charges against the individual responsible for failing to meet the requirements.
How to format your safety case report to meet standards?
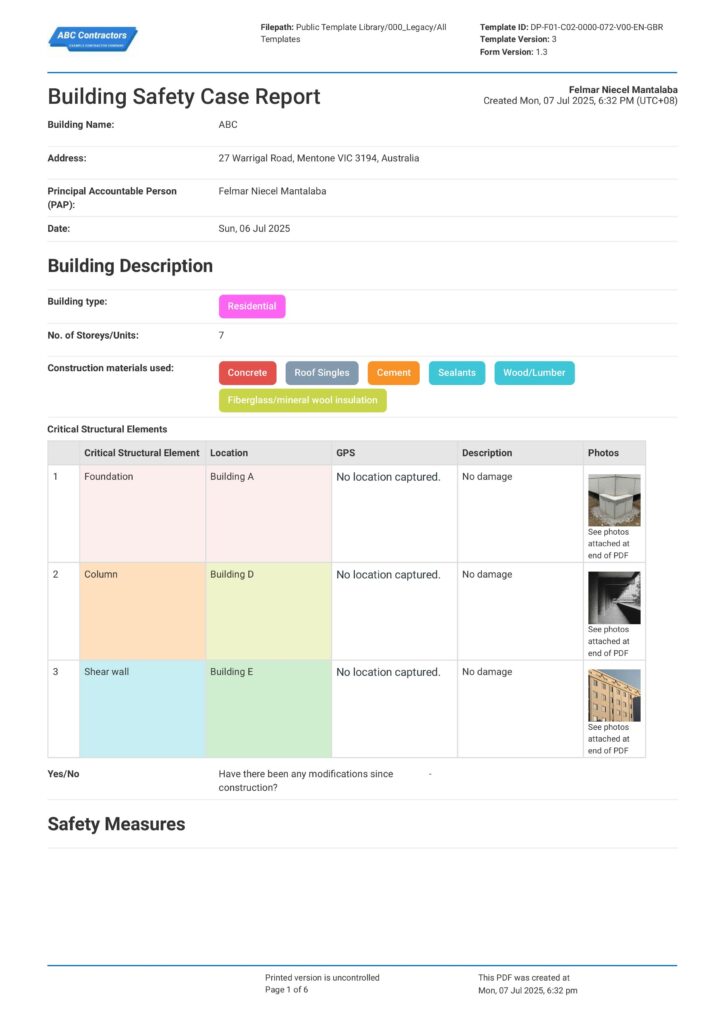
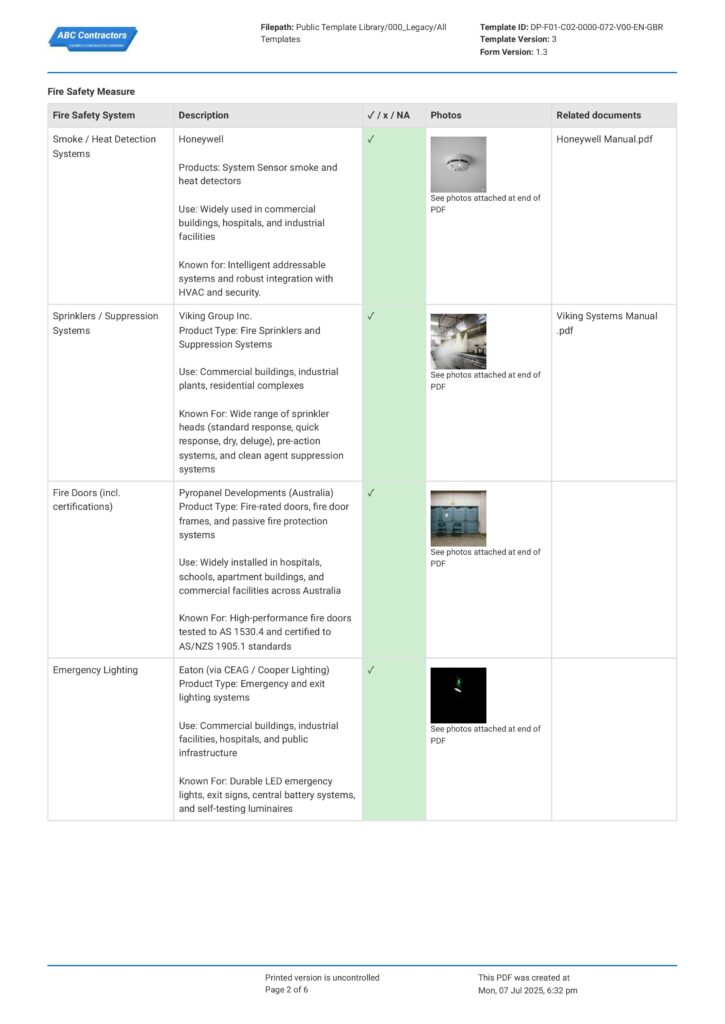
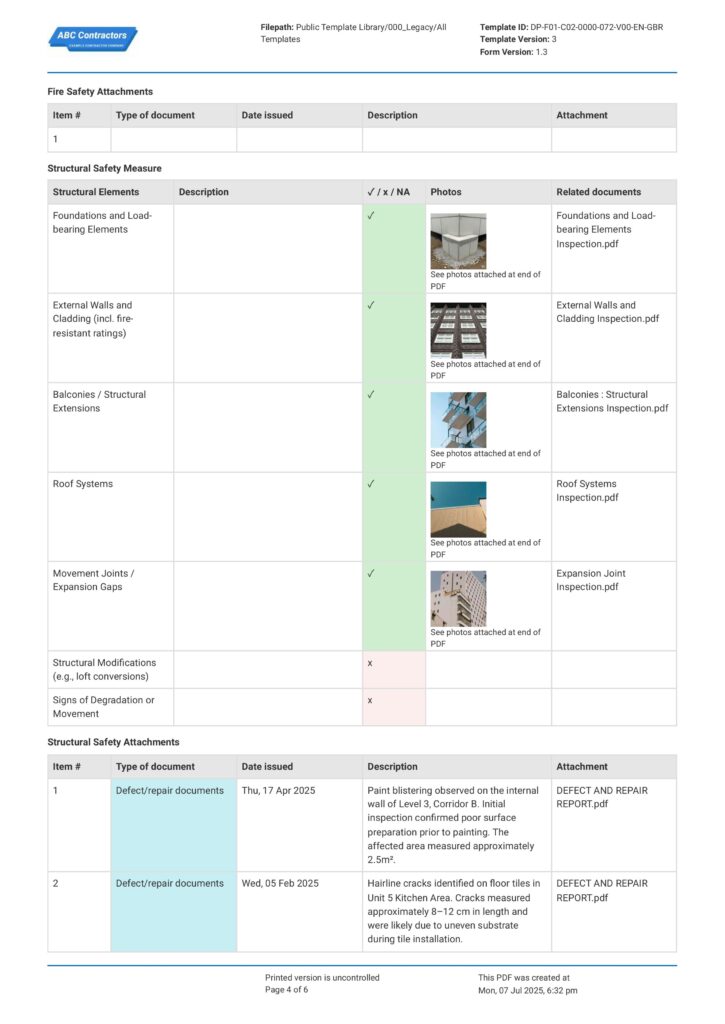
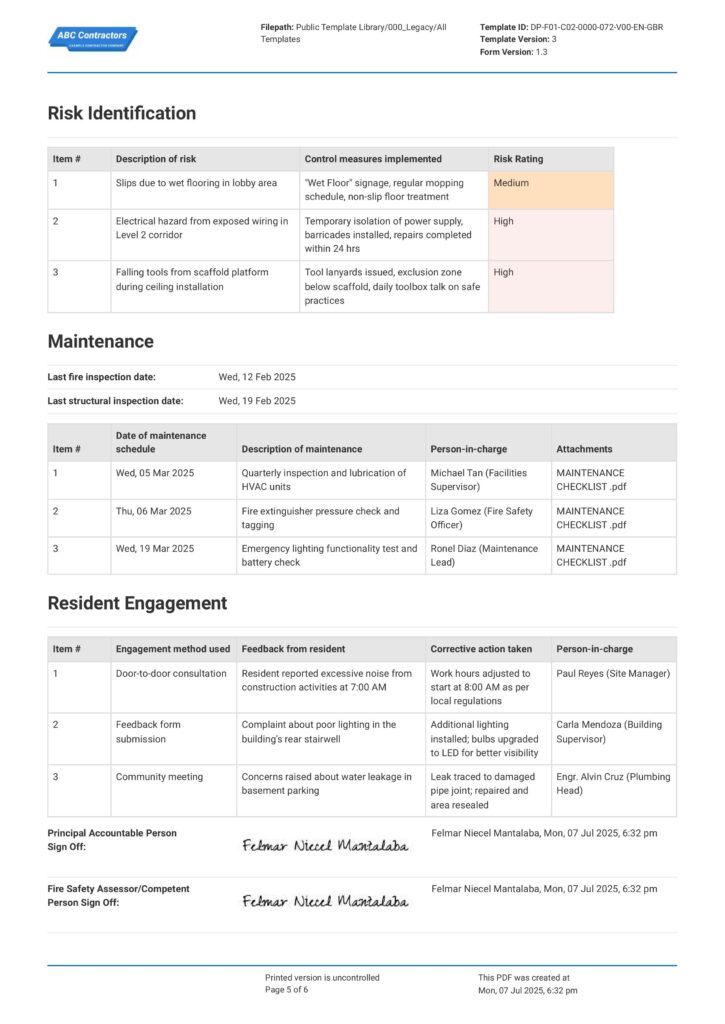
Complying and updating all the Building Safety Act documents is an intricate matter. You must present all the Building Safety Act 2022 documents in a clear, consistent, and traceable manner to easily check all complied records, track pending work, and enable smoother audits with the Building Safety Regulator (BSR).
Applying this system to your safety report helps you manage all the necessary regulatory requirements better. To understand how the formatting should look like, explore the given example below for a clearer picture.
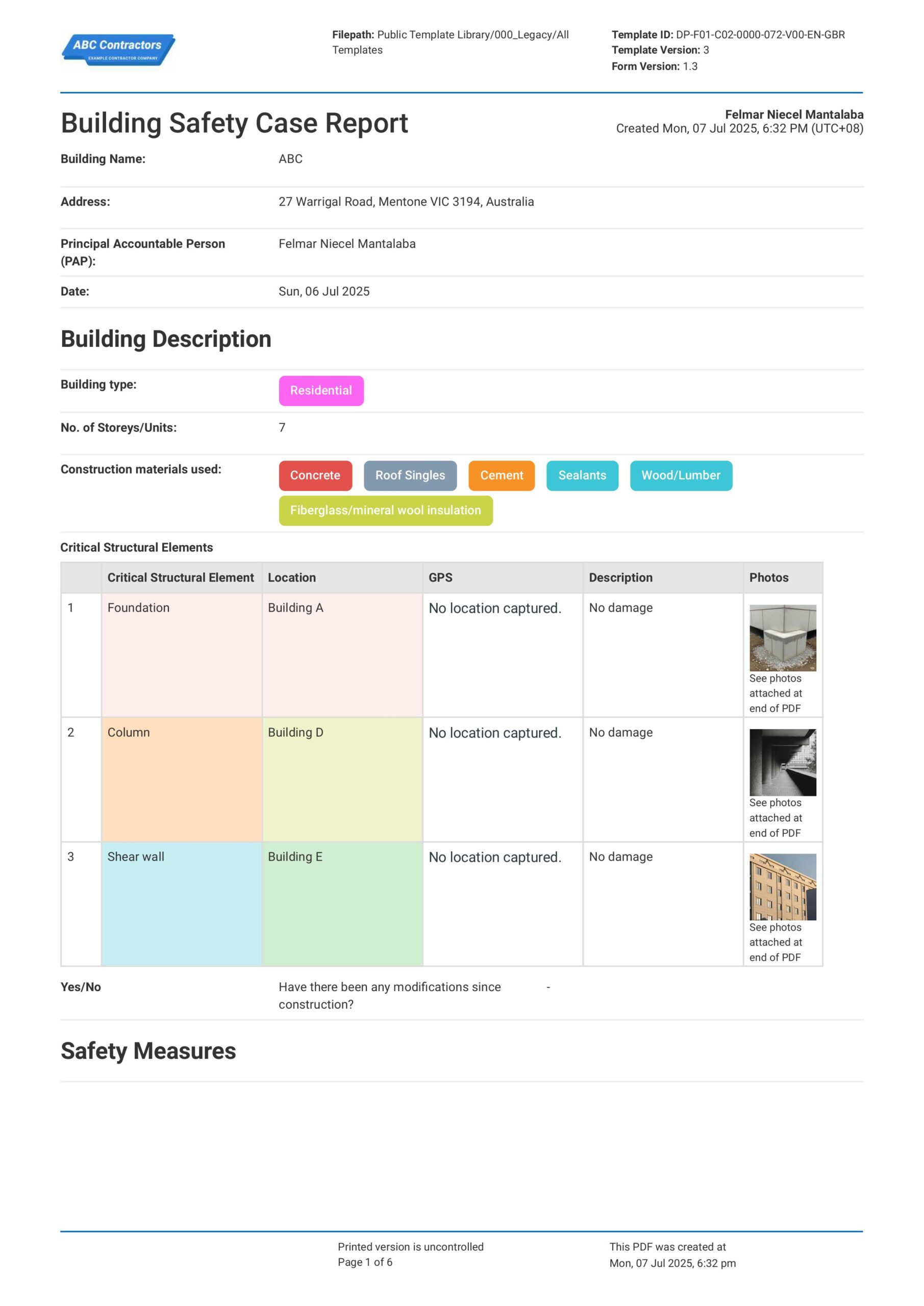
Use this Building Safety Case Report for free
What is the Building Safety Act UK?
The Building Safety Act UK is an important piece of legislation in the UK to improve the building safety across high-risk and high-risk buildings across England. For those who are seeking to understand the Building Safety Act meaning and what is the Building act, it's a framework that ensures safety in building design, construction, and occupation, and promotes accountability among dutyholders and persons involved.
The Building Safety Act of 2022 has six parts that address different elements of improving building safety. In this section of the article, we will be explaining what each part contains. This section aims to help you create a safety system that is both compliant with regulations and effective in practice. Here are the parts of the Building Safety Act of 2022.
Introduction
The introduction of the Building Safety Act outlines its legal foundation. It provides the building safety act definitions, such as "higher-risk" buildings, which are explained as buildings that are at least 18 meters tall or have 7 stories and contain a minimum of 2 residential units, and also establishes where the act would apply—mainly in England and some parts of Wales. Overall, the introduction explains the objectives of the act and provides directions on how people should perceive the provisions written in it.
Building Safety Regulator
This part introduces the Building Safety Regulators (BSR) and their responsibilities. The Health and Safety Executive enforced this position to effectively oversee building safety compliance. They will be the ones to monitor compliance through inspections, investigations, and sanctions. They also have a proactive role. They can intervene in providing solutions to found hazards in buildings before they turn into something much more problematic in the future. Overall, the BSR is a key role for ensuring safety standards for both new and old buildings.
Building Act of 1984 Amendments
The Building Act of 1984 was a legal act that set the minimum standards for constructions, extensions, renovations, and demolitions. However, upon reviewing these minimum standards, the outdated procedures of this act can no longer suffice with modern construction. The act requires amendment due to its weak oversight and lack of resident rights.
The new Building Safety Act of 2022 includes two key features that enhance the previous act. The first key feature is a gateway system, which imposes a strict safety review during the design, planning, and construction stages. The second key feature introduces the duty-holder roles, which provide accountability and ensure that hazards are always monitored and corrected. All of these amendments were created to improve the building safety systems.
Operation of Higher-Risk Buildings
This section of the Building Safety Act lays out provisions for the safety management of occupied buildings. The Act establishes guidelines for designating a Principal Accountable Person (PAP) and an Other Accountable Person. The PAP—usually building managers—should take the ultimate responsibility in creating and managing the safety system of the building.
Their responsibilities also include creating and logging building safety documents, appointing APs, and submitting reports to the BSR. All of these lead to the maintenance of the Golden Thread Information, which helps ensure that all safety documents, processes, and procedures are always accessible.
Read more about how the Golden Thread of Information and framework aids in the execution of the UK Building Safety Act in this article The Golden Thread UK Building Safety Act.
Safety Standards and Transparency
The Building Safety Act provides stronger protection for residents in all of England and Wales. This section includes reforms related to liability, redress, and transparency. One of the examples is the limitation period for the Defective Premises Act—an act where residents are compensated for dwelling in an unsafe building—is extended from 6 years to 30 years.
It also provides the Building Liability Orders where companies are still liable for their defective work even if they no longer exist. Finally, these provisions empower residents to report unsafe situations and request their correction. This legislation gives residents more power to hold contractors, developers, landlords, and building managers accountable for building defects and failures.
General Provisions
This section outlines the legal aspects of the act. The commencement clauses of this act have provisions for when the different sections of the act will come into effect. This section also lays out the enforcement powers and outlines the criminal and civil sanctions. Provisions that explain how government ministers can make secondary legislation—they can update and clarify certain parts of the act without the need for primary legislation—are also written in this section. All in all, this section ensures that the laws of the Building Safety Act are enforced and adapted in a timely manner.
Building Safety Act key points and other supporting UK regulations
Completely relying on the Building Safety Regulations will only get you halfway to truly building a solid safety system for your establishment. Understanding that there are regulations beyond the Building Safety Act is critical to providing continuous protection for the residents. Here are some important regulatory standards that you should look into when establishing your building safety framework.
Building Regulations 2010
The Building Regulations 2010 govern building construction and modification in England and Wales. The laws encourage energy efficiency, conservation, and building occupant health, safety, and welfare. Most of the provisions of this law address fire safety, ventilation, drainage, accessibility, structural stability, thermal insulation, and building design and construction.
It is also provided in this law that certain construction projects must be reported to the local authorities and fulfill specified requirements and processes. Most buildings, including houses, offices, schools, hospitals, and stores, fall under the scope of this regulation. They also cover gas, electricity, and heating installations.
Fire Safety Order 2005
The Regulatory Reform (Fire Safety) Order 2005, also known as the Fire Safety Order, is a piece of legislation in England and Wales that has replaced a variety of previous fire safety laws. The objective of the 2005 safety order was to streamline the current legislation and establish a standard for fire safety in all non-domestic properties.
The FSO is applicable to all workplaces and the common areas of buildings that contain two or more residences. It imposes legal obligations on the responsible person, who is typically the owner or landlord of these premises, to conduct and document a fire risk assessment and implement and maintain general fire precautions.
Health and Safety at Work Act 1974
The Health and Safety at Work, etc., Act 1974, often known as HSW, HSWA, HASAW 1974, or HASAWA, is a parliamentary act that establishes guidelines for workplace health and safety management in the United Kingdom. The statute outlines the broad responsibilities of employers, workers, property owners, managers, and maintainers for ensuring health and safety in the majority of workplaces. However, there are additional specific laws for industries such as construction and chemical manufacturing that operate in higher-risk environments. This is One of the main pieces of legislation established by the government is the act itself.
Compiling safety documents the easy and smart way
The Building Safety Act enforces strict compliance with the requirements. This implies that all Building Safety Act documents must be of high quality and completed promptly when necessary. However, when working with paper-based forms, things could get a little messy. Creating paper-based forms is time-consuming and requires significant space for compilation. This could lead to delays in providing safety measures and losing important documents in times of audit. This type of method is a hassle and doesn’t align with the Golden Thread of Information.
However, technology has got us covered. With the Site Audit App, you can now streamline and improve your building safety monitoring and audit records. Using this app, you can create forms and documents that align with standards, which you can easily fill and store in one place. This removes all the hassle of creating forms from scratch, printing them, and compiling them until they eat up all the office space. Additionally, you won't need to retype data on your computer anymore to produce your report. This app simplifies the process of creating a report with just a few clicks and taps.
Summary of UK Building Safety Act
The UK Building Safety Act of 2022 provides comprehensive provisions to ensure that higher-risk buildings are safe and free from hazards. By placing strong accountability on contractors, building managers, and landlords to create a safety system, the law continuously protects residents from any potential danger that might arise in the building, like what happened during the Grenfell Tower incident. However, these duty-holders must also consider other regulations to help build a more refined, complete, and solid safety system. Doing so doesn’t just make your building compliant but also makes your safety system genuinely effective and thorough.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is a compliance register required by the Building Safety Act?
Yes – a compliance register is required under the Building Safety Act 2022 in England. This register helps the Accountable Person keep track of all safety measures, inspections, and certifications for a building. You can stay compliant by regularly updating the register, keeping clear records of all safety-related actions, and using digital systems to make documentation easy to access and manage.
How is technology changing how people structure their regulatory requirements?
Technology is changing how people manage their regulatory requirements by replacing outdated paper records and manual tracking with digital systems like Dashpivot. This allows teams to streamline their processes, automate routine compliance checks, and keep everything ordered in one place. As a result, businesses save time, reduce errors, and make it much easier to stay compliant with regulations.
Does Sitemate offer templates for reporting building safety cases?
Yes - Sitemate offers ready-to-use and editable Building Safety Case Report Template that can also be edited for your workflow. Companies of all sizes in the construction and property management industry are using these templates right now to streamline their Building Safety Case reports. This helps them easily document safety risks, demonstrate compliance with legal duties, and keep all necessary records up-to-date and audit-ready.
Related resources

Mandatory Occurrence Report
Document and complete any occurrences in the workplace aligned with the UK Building Safety Act

Building Envelope Inspection Checklist
Detail and log issues and concerns of the building envelope with this inspection checklist.

Foundation Inspection Checklist
Easily inspect building foundations with a complete and fully editable template