Enviro – Types of hazardous waste: a complete summary

Types of hazardous waste you need to be aware of
What is hazardous waste?
Hazardous waste has two components to it. It must be a) considered waste and b) considered hazardous (surprise surprise).
Waste is a pretty common and well understood term, but because we are talking about science and environmental science, let's define what waste is:
Any item whoch the owner [of that item] no longer considers useful or needs to be discarded is considered waste.
The second part of this not so trcky puzzle is deciding what types of waste are considered hazardous, and require additional planning and thought around how they should be handled, moved, discared etc. Waste is considered hazardous if it meets one or more of the following requirements:
- Mixture contains a listed hazardous waste and a non-hazardous waste.
- Material meets the definition of one of the following:
- Ignitability (flashpoint < 60oC or supports combustion)
- Reactivity (e.g., water reactives, cyanides, explosives, unstable chemicals)
- Corrosivity (ph < 2 or > 12.5)
- TCLP toxicity (e.g., pesticides, heavy metals, organic compounds)
- Material is listed in 40CFR 261
- Material is not excluded from regulations.
So if your waste falls under any of these categories, it is definitely considered hazardous waste.
But while these parameters define what is hazardous waste, they don't give us good examples or reference points as to examples of hazardous waste or what hazardous waste usually looks like. This is often more helpful for making informed decisions about your waste in the future.
Types of hazardous waste categories
Hazardous waste doesn't have to be extremely toxic or obviously dangerous. In fact, some of the categories of hazardous waste are our every day items which we certainly don't consider hazardous.
The first category of hazardous waste which we will provide concrete examples from are characterised waste. Characterised waste is often the most common (and commonly recorded) waste found on industrial sites like construction, mining and oil and gas.
Types of characterised waste
1. Ignitability
Ignitable wastes have a flash point of less than 60 degrees celcius (140F), can be spontaneously combustible and create fires under specific conditions.
2. Corrosivity
Corrosive materials or wastes have a PH of:
- Less than or equal to 2
- Greater than or equal to 12.5
3. Reactivity
Reactive waste can cause gases, toxic fumes or explosions when heated, compressed or mixed with water; they are unstable under normal consitions and dangerous under a number of certain conditions.
4. Toxicity
Toxic materials are the ones most people think of when thinking about hazardous waste. Toxic materials can be harmful or worse lethal if absorbed or ingested.
Types of listed wastes
Depending on the associations, governments, agencies controlling waste in your area or region, there will be a certain number of listed wastes. For example, in the US, the EPA has a number of listed waste categories which you can read more about here including:
- F-list
- K-list
- P-list and U-list
Types universal waste
Universal waste items are the common items and household items people use to get their jobs done which often pose the greatest risk of poor handling or incorrect discarding.
This category includes items like batteries, lamps and equipment containing mercury and pesticides.
Types of E-waste
E-waste has become more important and a larger proportion of hazardous waste in the last few years because of the prevalence of electronic items including computers, laptops, phones, tablets and fridges.
While it may seem easy enough to consider these items common and non-hazardous, the reality of E-waste and the process which creates electronic items means that they are indeed hazardous and need to be consciously exposed of.
Types of industrial based hazardous waste
To give you a few examples of the types of waste found on many industrial sites and within many industrial organisations, we have outlined a few common cases as well the hazardous waste management plan forms that each require to be recorded, handled and disposed of correctly.
Use and customise this hazardous waste management plan for free.
Ignitability (flammable)
Ignitable materials will often come up in hazardous waste management plans, and can be found anywhere on site and associated with any type of activity - such as excavation.

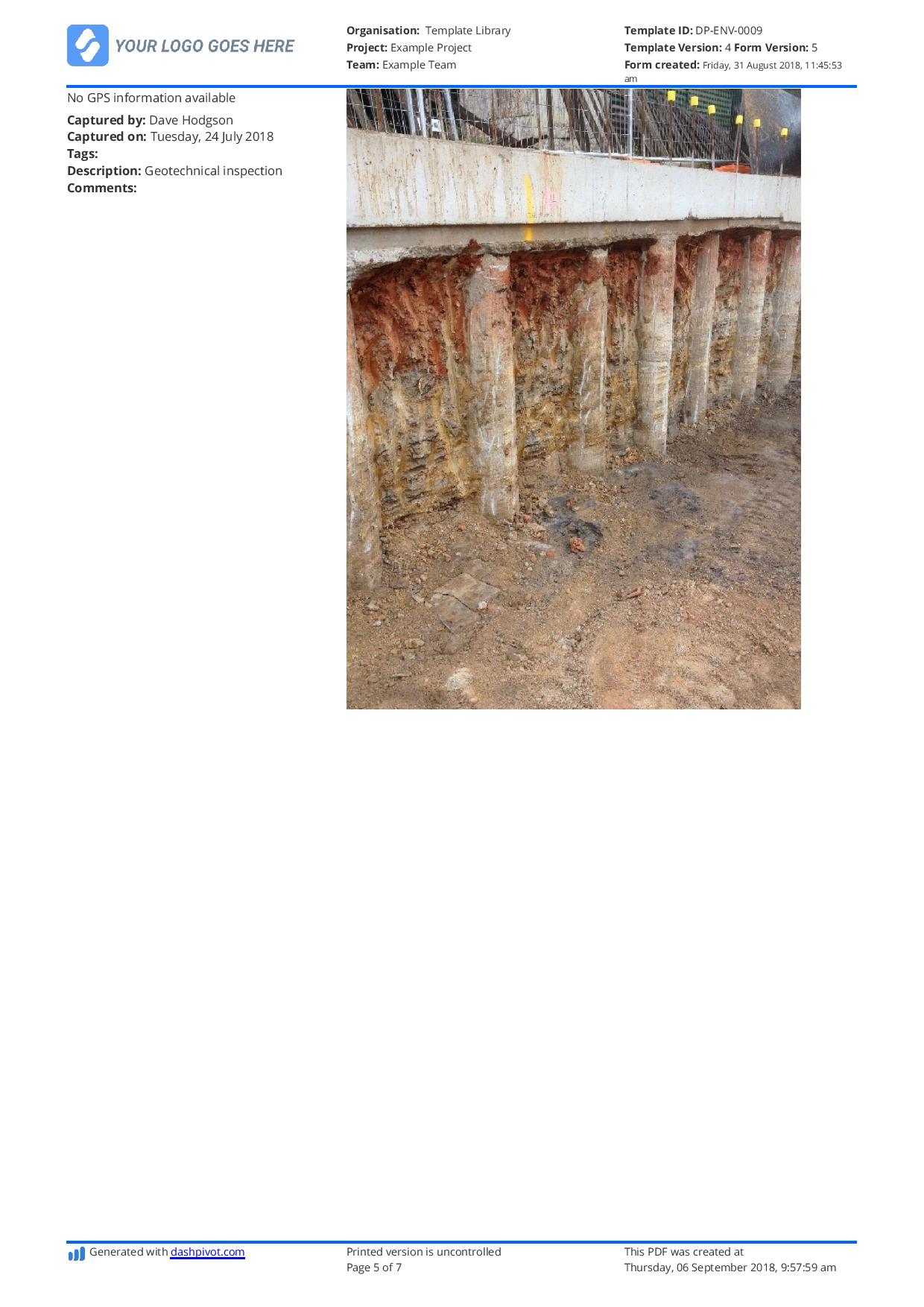
Corrosivity (rusting)
Corrosive materials are also very commonplace on site. They can impact specific materials or have a negative impact on entire projects and works if not handled and disposed of properly.

Looking to manage your hazardous waste more effectively?
If you are looking to improve the way you or your company handles hazardous, treats and documents hazardous waste, take a look at our free templates below.
The templates are smarter than excel or word, and enable you to manage work in the cloud, where it is always accessible, secure and more efficient.

Hazardous Waste Management Plan template
Plan and manage hazardous waste more effectively to keep your projects and sites running smoothly and cleanly. See the template →