Dashpivot article – Health and Safety Plan example
Health and Safety Plan Example
This article teaches you how to create an effective Health and Safety plan by using the proper example as guide. We'll show you helpful ways to develop a compliant one based on your high-risk industry, type of work, and by staying updated with the latest regulatory changes.

Table of Contents
Article Summary
- A flexible Health and Safety Plan is ideal for high-risk industries due to its live document nature that matches with the evolving risks in industries. Make sure that the contents of your HSPs align with the relevant regulations, the specific industry, work type, and other factors.
- The core key areas in a Health and Safety Plan should be drafted with practical and actionable contents. Focus on hazard identification, control measures, training and safety discussions, and monitoring processes.
- Regulations change as the industries evolve over the years. It's key to stay updated with the local regulations and align the contents of your HSP to those changes. Make your HSPs and safety practices are compliant, effective, and relevant all throughout the project lifecycle.
What makes an effective Health and Safety Plan?
A Health and Safety Plan is a document that lays down the proper procedures in fulfilling the project, in the safest way possible. It includes the roles and responsibilities of each personnel, the hazard identification before even a project starts, their risk assessments and control measures, or anything under the sun that makes the project safe to do. They’re especially helpful in high-risk environments like construction, manufacturing, oil & gas, mining, and many more.
To make your HSP truly effective, you should go beyond the surface-level compliance or even beyond than just creating one for the sake of it. Make it practical and actionable.
Health and Safety Plan Example Format
Develop a compliant Health and Safety Plan (HSP) that aligns with the regulatory requirements according to your type of industry, work, setting, and other factors. The contents vary significantly depending on those factors plus the regulatory requirements you’re following. For example, in the construction industry, you’ll have HSPs for operating on equipment, but for oil and gas, you’re focusing more on hazardous substances.
That’s precisely why your Health and Safety Plan should be flexible and adaptable. You need a flexible format just like the example below to tailor it to your needs as a business – whichever industry you’re in, what type of activities you’ll be working on, and other factors. Make compliance easier, and be prepared across different project types by checking the example right below here.
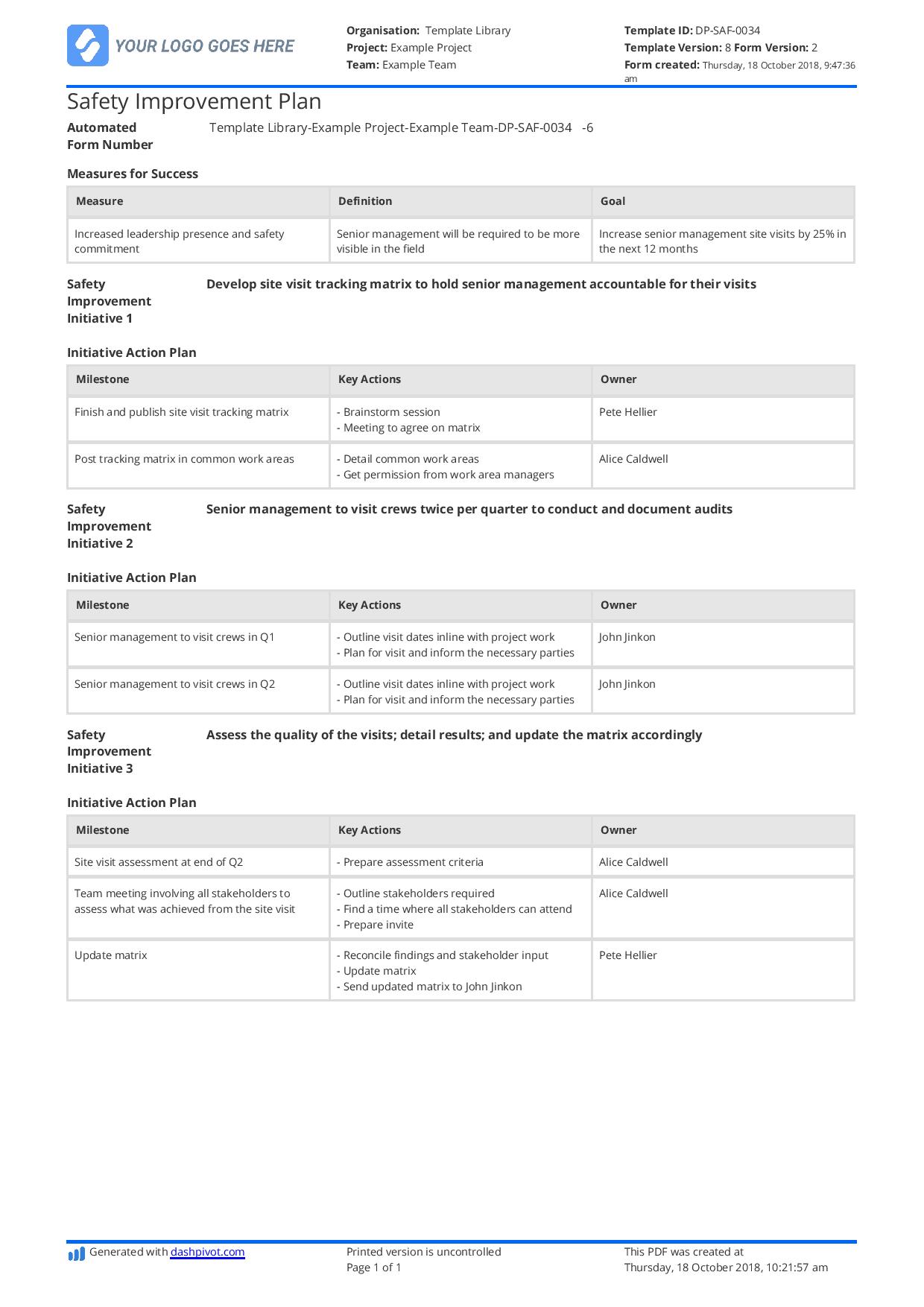
Use this Health and Safety Plan for free
How to effectively cover the core elements of your HSP?
Major core elements build and define the very principle of what a Health and Safety Plan is. In order to effectively draft your HSP, it's key to build those elements with intention and purpose. Focus on the key areas like hazard identification/risk management, the training, and even the monitoring procedures. Here are some important pointers in each core element, coming from the best practices in the industry, that you should definitely implement in your Health and Safety Plan:
Hazard identification, risk assessment, and control measures
In the preliminary stages of the project (prior to starting the actual work activities), anticipate the associated risks from the planned activities, the condition of the worksite, the equipment to be used by the workers, and other external factors. It’s best to develop control measures based on those anticipations to prepare in case they do happen.
A Health and Safety Plan being a live document, means along the way, you’ll have to update its contents. Some risks and hazards are discovered along the way once the project is active, so it’s best to prepare for any unforeseen circumstances. These sections should also be continuously updated, most especially the control measures – to make sure they’re being performed and monitored.
Here are some related articles that can fuel your knowledge in these sections: What is a Task Hazard Analysis?, Purpose of a risk register: Here’s what a risk register is used for, Risk log: Everything you need to know about risk logs, and Risk monitoring and control: How to make yours better and safer.
Training your workers
Before even starting work, conduct briefings, discussions, and if necessary, training, before they begin. These could be toolbox talks, or if the task is very specific, then conduct role-specific training. Make sure that workers know the risks, the proper procedure in performing the task, and the safety protocols. Begin a culture of safety even before day one.
These are key articles that can aid you in knowing the right safety discussions for high-risk industries and specific projects, tasks, or jobs: Pre-Job Brief Example, 1 minute safety talks, Engineering Safety Moments, and Toolbox Talk Ideas.
Monitoring procedures for updates and long-term effectivity
If you’ve got control measures in place, then it should be paired up with the monitoring procedures to see if those control measures are effective. Set up flows or systems for inspections and performance reviews. See if they’re not just band-aid solutions, but long-term ones. Your team could develop and mandate reporting procedures for incidents and near misses, and assign persons responsible for overseeing the safety standards in the workplace or even across all levels of the company.
Read more on these relevant articles to gain more insight how to monitor control measures, incident reporting, and many more: Why is it important to keep records of site inspections?, Incident investigation report sample - and what else you need to know, What is considered a near miss?, and How to make a Near Miss Report.
2024-2025 updates impacting Health and Safety Plans
Aside from Health and Safety Plans being live documents, the regulations that they are based from are also ever-changing and evolving. They’re always being updated to cater to new workplaces challenges. Two of the most notable updates are:
Hazard Communication Standard (HazCom)
Effective as of July 19, 2024, OSHA published to enhance the classification and labelling of chemicals. Hazard information should be complete, easily understandable, and accessible to workers and first aid responders.
Read more on: OSHA’S Final Rule to Amend the Hazard Communication Standard, and Department of Labor Announces Final Rule Updating the Hazard Communication Standard to Better Protect Workers, First Responders.
PPE Fit Requirements for Construction
Effective as of January 13, 2025, PPE must properly fit each worker in the construction site.
Read more on: Protective Equipment in Construction: Final rule.
What are the implications for employers and companies, then?
- You should always review and revise your policies to align with the latest updates that affect how you structure your Health and Safety Plans, or even the contents of your HSP.
- When regulations change, so should the discussions, briefings, talks, and training sessions for your employees. Relay those updates in an orderly manner so all of your workers can stay on top of the regulatory changes.
- To make sure that regulatory bodies won’t question your operations, it’s best to conduct internal audits and inspections. Regularly assess your own workplace conditions, and make sure that they’re up to standard.
Enhancing your own HSP through digital solutions
Instead of just simply and passively copying off a format of an HSP example, make sure that you’re also writing one with proper intent and awareness. To aid you with that mindset, streamline your safety processes using digital solutions. They do more than just making things fast. They help you build out and enhance the core elements and sections of your HSP.
A risk assessment software can aid you in easily logging in the hazards and conduct risk assessments in real time. An incident report software and a near miss reporting app make logging incidents convenient and accessible to everyone, encouraging a blame-free and safety culture. You can easily conduct trainings to workers and keep track of attendance using a training and qualification records app. Use this safety app to make sure all safety protocols, briefs, discussions, and talks are well-documented and relayed to each one before work begins. These apps and software make it so much easier on your end to deploy your Health and Safety Plans across teams and sites.
Summary of Health and Safety Plan Example
The given example in the earlier part of this article helps you draft your own Health and Safety Plan, but you must also actively write one where the core elements are properly thought. Format your HSP with properly structured hazard identification/risk assessment/control measures section, training, and monitoring sections. Additionally, being updated on the latest changes regarding health and safety helps keep your HSPs relevant.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is a Health and Safety Plan required in all high-risk industries?
Agencies like the International Labour Organzation (ILO) provide guidelines and best practices in making sure a workplace is healthy and safe for workers. Regulatory bodies base off their regulations from such agencies, and a Health and Safety Plan perfectly meets the principles and objectives ILO tries to share worldwide and is considered as a supporting document to meet regulations.
How is modern technology shaping how people draft their Health and Safety Plans and other safety documents?
As industries progress, technology tries to catch up and meet the evolving challenges and risks. Technology fully transforms how documents are being managed. From paper-based documentation, digital tools like Dashpivot replaces that into digital forms. Teams can fill out documents using their devices, fully automating the data entry process. This makes sure data is accurate and secured. This leads to better data analytics, safer worksites, and more accountable employees.
Does Sitemate offer templates for Health and Safety Plans and other relevant safety documents?
Yes - Sitemate offers flexible and easily editable templates like this Safety Improvement Plan and other safety forms. Companies of all sizes across various industries are using these templates right now to streamline their Health and Safety Plans, and other safety processes.
Related resources

Safe Work Procedure
Keep people following safe every day work procedures, with ease.

Site Specific Induction
Speed up your site induction process to keep people and projects moving forward quickly - and in an organised manner.

Weekly Safety Inspection Checklist
Get your weekly safety inspections done easier and faster, and then keep them all organised and easily searchable.