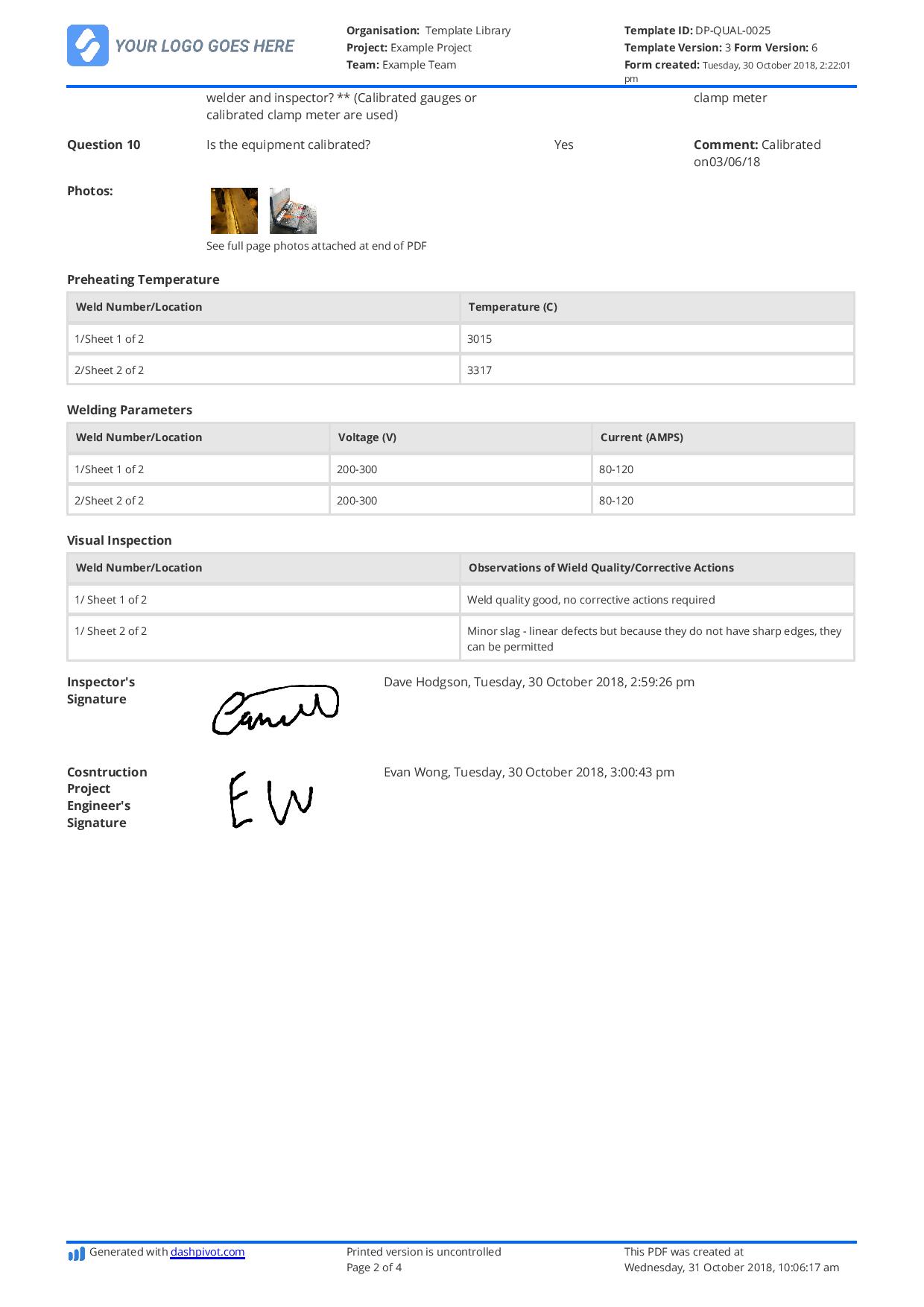
Dashpivot Article – OSHA Welding Safety Requirements
OSHA Welding Safety Requirements
In this post, learn about the OSHA welding safety requirements - covering essential standards, protective measures, and best practices to ensure workplace safety and compliance for any type of welding activity.
The Hazards of Welding
Welding is a common activity done by many industries to fabricate or repair equipment and machines. This has been a necessity for many industries, but despite its need, it also brings with it common welding hazards that organisations need to be aware of. It's for this reason that there are a number of OSHA welding safety requirements.
Welding hazards are not bound to just the welder themselves but also to the people around the vicinity where the activity is taking place. Fortunately, these hazards can be controlled to prevent unwanted accidents as long as you are aware of them.
Here are some common hazards that are present during a welding activity:
Welder's Flash
A common term in the industry for photokeratitis. The disorder is typified by symptoms including sensitivity to light, headache, redness and pain in the eyes, impaired or transient vision loss, and swelling in the vicinity of the eyes. This occurs when the iris of an individual is directly exposed to UV radiation. A welder's flash is an inevitable consequence of workers' refusal to wear a welding mask or their inappropriate use of it in welding.Personnel who merely observe the welding process may also be susceptible to photokeratitis.
Burns
The process of welding is to melt the filler metal to solder two metal pieces together. To melt this filler metal, temperatures could reach 1000 degrees Celsius or more. Because of this, it is possible for welders to be susceptible to burns. Burns mostly occur due to bad practice. One common example that might lead for welders to get burn injuries is due to skipping procedural precautions to finish faster. Another example of where workers get burn injuries is due to not wearing PPE and wearing improper PPE. It is important to remember that our skin can start to sustain burn injuries at 44°C and welding can reach up to more than 1000°C, so better think twice when you decide not to wear PPE or wear the wrong PPE.
Inhilations of Fumes and Gases
You will be exposed to invisible gaseous fumes when welding, such as carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, chromium and nickel oxides, and ozone, all of which can readily enter your lungs. The resulting harm may be severe, depending on the gas or fume, concentration, and length of exposure. Welding fume has no minimum safe exposure limit. Legally, employers must efficiently limit workers' exposure to all forms of welding fume, including mild steel welding fume.The following diseases may result from inhaling these fumes: asthma, pneumonia, metal fume fever, throat and lung irritation, and cancer.
Fires and Explosions
These are common hazards when doing activities that involve hotworks. When welding, sparks are inevitable to fly off when soldering two metals. These sparks could fly off to materials that could easily burn or ignite. Having said this, it can easily be pointed out that these hazards would likely occur when performing welding in a disorganised and messy area that is full of combustible materials.
Electricution
Most of the welding machines today are powered by electricity, and these machines run on high amperage that could prove harmful to humans. This hazard can further escalate if worker's are working in areas that are damp, have metal flooring, and are in cramped conditions. Shocks are also likely to happen if the welding machine or parts are in poor condition. One good example of this is a peeled-off wire. An accidental touch of this could really sustain unwanted injuries.
Taking Precautions by Inspecting Smartly
One way of protecting yourself and your workers is to identify the hazards before proceeding to the welding activity. Having awareness of these hazards can help you provide the appropriate measures to eliminate them. The most effective way to be aware of these hazards is through inspection or risk assessment forms like a Welding Safe Work Method Statement.
A thorough and detailed inspection can provide us with the information to procure the correct and appropriate safety measures required. Furthermore, compiling these inspections could provide us with enough statistics on what hazards are a common occurrence and what hazards are not, which gives us an advantage in placing appropriate funding on materials needed to keep the company safe for workers. Part of the power of OSHA's welding safety requirements is that they were built from detailed data and observation over time.
Regular inspections can be a bit of a hassle and somehow time-consuming, especially when doing it in the pen and paper process. Inspecting this way also invites a lot of human errors in the event that data is transferred to a computer. The only way to eliminate this is constant double-checking, which consumes a lot of time. The pen and paper method also isn't helpful to our environment since paper and ink are constants.
But what if we told you that there is a smarter way to do the inspection that eliminates all those problematic things with the pen and paper method? With this new modern approach, your inspection process could be streamlined without the struggle and hassle of transferring data to your computer. This method uses a digitalised form that can easily be uploaded and shared with the necessary employees. The best part of this method is that you need not worry about staying online to complete the inspection. If you want to check this smart method out, please see an example of a form made below made by the software that could help improve your inspection process.
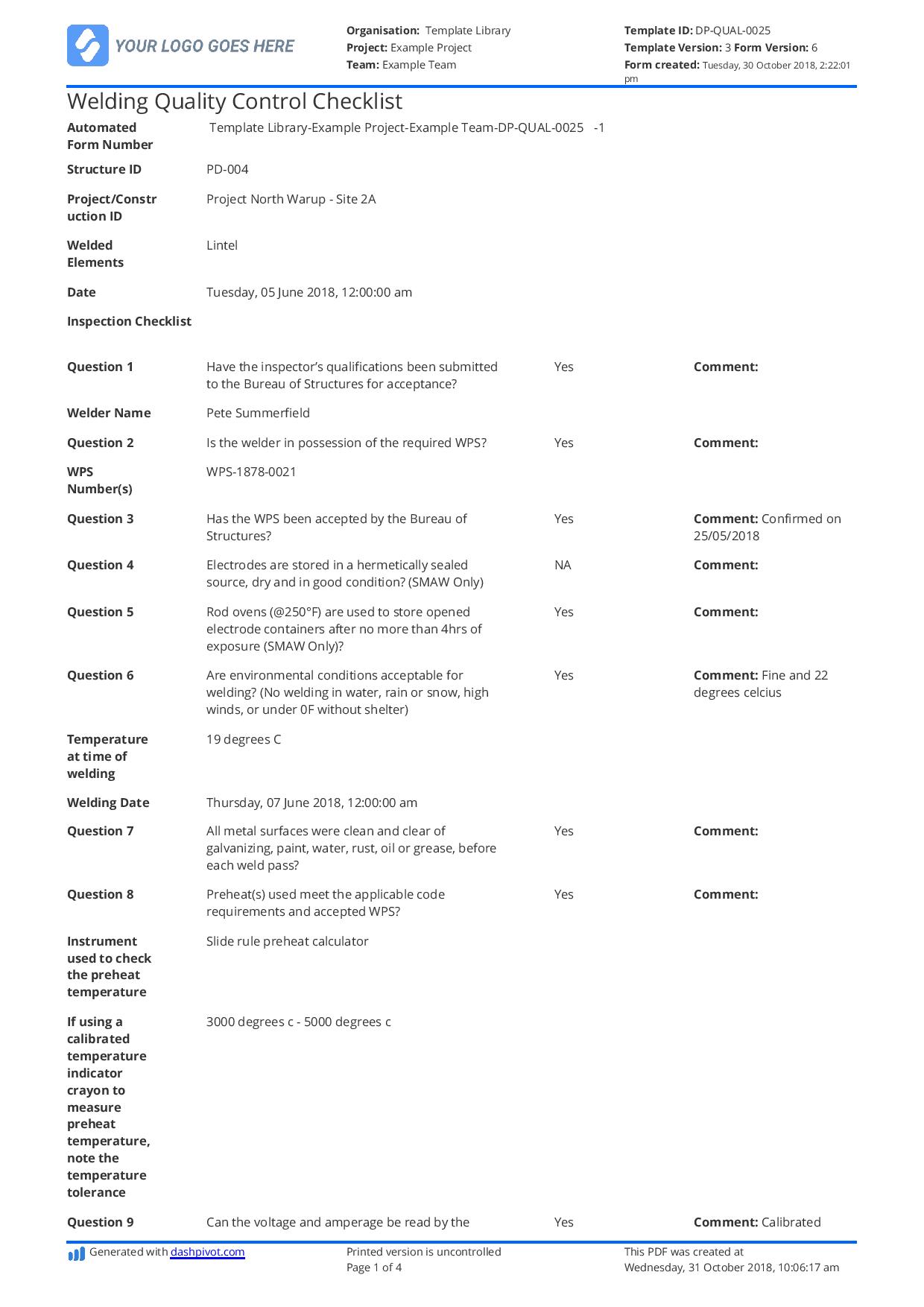
Use this Welding Quality Control checklist for free
Why did OSHA Provide Welding Safety Requirements?
We have established that while welding is an activity that is commonly used in any industry to fabricate and fix equipment, it also brings along hazards that have the potential to harm humans. So having said that, it is very likely that the Occupational Safety and Health Association (OSHA) did something about this.
Being a federal organisation that ensures safe and healthy work conditions, one would likely put their heads around to make sure standards are established for organisations to follow in order to safeguard the employees when doing the welding activity. Having standards means having a procedure that is widely accepted, safe, consistent, and efficient. Welding itself as a number of common procedures which dramatically reduce of welding issues, like Welder Qualification Tests (WQT) forms.
It's these safe guards which drive improvement and safety in high risk activities like welding, hence the OSHA welding safety requirements. So in conclusion, these standards were made for the benefit of organisations to have a safe and secure process.
What are the OSHA Welding Safety Requirements?
OSHA PPE Requirements for Welding
OSHA has detailed rules about how to be safe when cutting, welding, and brazing. This part mostly talks about guidelines for PPE and PPE training. In 1910 Subpart I, sections 1910.132, 1910.133, 1910.134 (appendices A through D), 1910.135, and 1910.138 spell out OSHA's rules for personal protective equipment (PPE) used in welding. These rules cover both general safety measures and special safeguards for the eyes and face, the lungs, the hands, feet, and the head.
1910.133, which talks about eye and face safety, has the most important rules for welders. This part talks about the different ways to weld, the sizes of the electrodes, the current that is used, and the smallest amount of shade that is needed to keep the eyes safe from the radiation. OSHA regulations mandate that companies ensure their workers have appropriate eye and face protection against flying objects, molten metal, chemical vapours, and harmful light radiation. In this part, OSHA gives advice on how to set the shade so that it starts out too dark to see the weld area and then gradually gets lighter. The person doing the welding is the only one who can decide how to set the eye shade. They can make it as comfortable as they want as long as it meets the basic requirements.
OSHA on Ventilation Requirements for Welding
OSHA's rules on weld airflow depend on three things: the number of welders in a building, the metal being worked with, and the size of the area where the welding is taking place. The need for weld fume exhaust control goes up as the number of welders goes up, and respirators are enough for the welder.
One more thing to think about is the metal that is being used. The most common result of welding in the U.S. is hexavalent chromium, which is also one of the most common and dangerous chemicals in weld fumes. If the roof is less than 16 feet high, OSHA says that the area where welding takes place must have air flow. Weld aeration should happen no matter how high the room is, though, for the best air quality. Larger air movers, like fans or blowers, work best in bigger rooms. For smaller rooms, a gas source capture system will work better.
OSHA on Fire Prevention Measures during Welding
Standard 1910.252 provides guidance on how to prevent fires in buildings and manufacturing facilities. Additional welding concerns for building ships while they are at sea are included in Standards 1915, subpart D 1915.51 through 1915.57.
For welders, the first guideline contains the most helpful general information regarding preventing fires. Because this standard includes more than just the risks associated with hot work, it is crucial that all welders study it carefully.
According to the OSHA guideline, all combustible items, such as cardboard, insulation, and flammable gases and liquids, shall be removed from areas where hot work will be performed before welding or other hot work begins. They must be maintained away from sparks or flames that could cause them to catch fire if they cannot be removed. Welders should be very aware of these guidelines because combustible materials aren't usually obvious.
The most hazardous source of combustible materials is frequently the welder's own oxyacetylene cutting apparatus. Welders frequently lose sight of the location of the gas supply lines in relation to the cutting torch or the arc welder's spark drop. Additionally, combustible compounds and residual vapours may be present in work equipment like pipes and drums. The possibility of hazardous compounds in the air is likewise covered by standard 1910.252. Chromium, which is frequently added to steel alloys, is one of these.
OSHA Training on Welding
Comprehensive training on the risks associated with welding operations is required by OSHA standard 29 CFR 1910.252(d):
Employers are required to provide their staff with safe fuel gas handling training for brazing, cutting, and welding. Employers must explain the facts and be aware of them in order to provide such training. Workers should also be aware of how welding safety hazards are interactive.
Employers must also supply operating equipment that complies with OSHA welding safety regulations and use an OSHA-compliant welding equipment checklist to perform the necessary testing on that equipment. Employers also supervise the safe handling, transportation, and storage of gasoline cylinders.
Reinforcing Compliance with OSHA Welding Safety Requirements
Any company that wishes to make sure it complies with all applicable rules and OSHA welding safety requirements must implement a compliance audit procedure. Before there are financial or legal repercussions, these audits assist businesses in identifying potential weak points and taking remedial measures. A compliance audit thoroughly examines the rules, methods, and operations of a business.
In doing an audit, the more detailed it is, the more gaps are identified and closed. A good example of doing a detailed audit is to do it digitally with our platform. With this, you can take photos from the quality assurance auditing app and automatically add timestamps, geotagging, markup, and smart tags.
More frequent audits are advised and could prove to be more helpful for organisations. However, doing audits takes a lot of time, especially if you're doing it traditionally. However, doing it on a digital platform, you can conduct regular quality audits to find areas for improvement. You could also avoid costly rework with the back and forth communication to chase up missing information.
Using a digital platform, the hassle of inputting data to your computer is already eliminated. You can quickly share completed quality audits in one click. Shared reports are professionally formatted PDF or CSV with your logo and brand colours.
Build digital processes around your OSHA Welding Safety Requirements
A dedicated OSHA Welding Safety Requirements app can add extra functionality and features that save you time and make your work more efficient.
Scan your team's digital IDs to automatically add their name and signatures to the document for easy sign-ons.
Automated workflows make it easy to draft, conduct, and sign off on OSHA welding safety requirements audits with automatic notifications to relevant team members so nothing is ever missed.

Take 5 template
Document and store your take 5s with ease using this template

Fatigue Management template
Ensure welders aren't fatigued with this safety check form

Pre-Start template
Run pre starts more efficiently with this streamlined process