Finance – Project cost management

Project cost management
Project cost management definition
Project cost management involves all of the elements of project management which relate to budget and costs, including estimating, allocating and tracking and controlling the costs of a project.
These project cost management activities combine to enable a project-based company to predict, project and control expenses in order to deliver a project on budget.
One of the hardest parts of running any project is that there are a number of internal and external forces at play, and these forces and influences can quickly wreak havoc on even the best laid plans.
There are three main components of project cost management on any project:
- First, the projects approved costs (or budget at completion) is calculated before the project actually begins
- Second, the company and teams document and track progress in order to provide up-to-date data on project costs and cost variance so that the company can course-correct and keep the project on budget
- Lastly and once the project is complete, the company will compare the planned vs. actual data from the project and use this information to inform their next project budgets and plans
Project cost management can be a very involved process and carries a lot of importance and risk for all companies, so it's imperative that a company has the best understanding, processes and tools possible to plan and execute their cost management strategy well.
Without good project cost management, project budgets can quickly blow out of control and companies can quickly lose money and put themselves in a lot of trouble.
The project management cost estimation
Project management cost estimation is arguably the most important aspect of cost management, because it sets the budget and tone for the rest of the project (this is the number/s the rest of the project is judged by), and has a huge influence over whether the company makes or loses money once the project or phase of work is complete.
A project lives and dies by its initial budget, and it sets an early and heavy anchor which can not be released later in the project.
Project cost estimation is part art and part science, and involves forecasting all of the resources needed to complete a project within the defined scope of works. Most companies incur some direct and some indirect costs in delivering a project. For most companies, these costs and resources include:
- Labour - The cost of human labour on a project
- Materials and equipment - The cost of the other resources required to deliver a project including plant, assets and equipment. These costs have continued to increase in recent years with the continued rise of 'capital' intensive and technology driven projects
- Facilities - The costs associated with using work spaces and facilities not owned by the organisation
- Vendors - In many project-based industries like construction, a single company almost never delivers a project alone. These projects require the services many different contractors and subcontractors who specialise in specific activities. These 'vendors' and 3rd parties also need to be factored into project costs.
- Risk - Risk costs can include contingency plans and other elements which reduce risk for companies.
Combining these (and any other applicable resources) results in a total cost estimation for a project.
The initial project cost estimation which a person or company creates often dictates whether or not a company moves forward with a particular project at the tendering or proposal stage, so getting your estimates as accurate as possible is crucial to choosing and delivering the right projects.
Establishing a project cost management plan
A cost management plan is exactly what is sounds like, and is the crucial connection between the project cost management estimation and actual project delivery.
A cost management plan includes information regarding the projects estimation, and then also includes information on how these costs will be allocated and controlled during the course of the project.
The cost plan often serves as the safety net for a project by analysing and providing a framework for how the project is and will be funded.
The typical 'main' components of a cost management plan are:
Control thresholds
Control thresholds ensure that a project doesn't go too far over budget. These thresholds set the minimum and maximum cost variation standards so that when the project costs fluctuate away from the initial budget by too much, they are quickly bought back under control through specified means.
Levels of precision
Many of the projects which need to be most concerned with project cost management are managing projects with many zeros in the budget. Levels of precision are very important over the course of thousands of numbers and calculations, so it's important to set these levels of precision at the outset of the project and communicate them to all the necessary stakeholders.
Units of measurement
Similar to the above levels of precision outlined in the project cost management plan, the units of measurement will also need to be declared and agreed to in the plan. This is obvious, as minor changes in units of measurement can wreak havocs on derivations and can also make data reconciliation and using the data very difficult.
Reporting formats
The project cost management plan will also set out how information will be reported on during the course of a project. The frequency and format of reports can have a drastic impact on the level of detail and accuracy being passed from project delivery to project management.
Companies who use document management systems can often avoid this step as their reporting formats are standardised and templatised across the organisation or individual projects and teams.
Rules of performance measurement
Rules of performance measurement are incredibly important for gauging progress and performance through earned value management and other project management techniques. Rules of performance measurement sets the framework for how each project activity will be considered and measured e.g whether a phase of works is 50% complete or 55% complete depends on how you measure progress. Some companies set their rules as being that the entire activity be complete, whilst others work on a partial completion basis.
Project cost management examples
This section is designed to provide you with a brief overview of the different types of project cost management techniques you may come across, as well as show you a specific example of a project cost management technique in practice.
We have already covered a couple of the major project cost management examples in estimating and planning.
Some of the other examples you will see include:
Analysis - Project managers and companies have a number of cost analysis tools at their disposal. Some of these include basic cost-benefit analysis and more detailed cost effectiveness calculations.
Budgeting - Budgeting is an obvious and important aspect of project cost management. Some of the budgeting tools and controls which have the biggest impact on costs include the development, approval and controlling of budgets.
Procurement - One of the ways in which projects costs can creep out of control is through poor procurement practices and unapproved purchases. This can be the ordering of items which didn't need to be ordered, but more often than not, it's simply the ordering of goods and services through non-approved suppliers. Companies work hard to negotiate good prices with vendors and suppliers they trust, and when a supervisor or worker buys something through a different supplier, it can cost more and put the quality of work at risk too.
Having good project cost management controls through the procurement and supply chain is really important for keeping material and service costs on budget.
Financial controls - Financial controls are very important for project cost management. Properly segregating duties for submitting and approving financial activities as well as having the right internal auditing procedures in place creates the checks and balances every organisation needs.
Resource management - There is a lot of resource movement and management in all projects. An important part of project cost control is controlling all resources including waste and other materials. Managing these resources efficiently can really reduce overhead and logistics costs.
Governance - Having some level of governance or hierarchy can be really important for cost control. A project governance board who can cut off funding for a project which is over budget or failing to meet objectives can keep everyone on their toes and prevent worst case scenarios.
Project cost management techniques
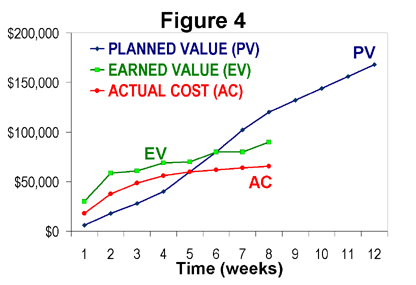
One of the most used and useful project cost management techniques is earned value management. Earned value management enables a project manager or company to measure cost and schedule performance throughout the life of a project.
While there are a number of different earned value metrics, the one we care most about specifically for project cost management is cost variance.
Project management cost variance
Cost variance takes our earned value calculation and subtracts the actual costs incurred on the project thus far.
What this is doing is taking the amount of earned value we have generated today, and subtracting the costs we have incurred to create this value.
This is going to tell is whether we are over budget or under budget, while the other earned value metrics help us understand how we are performing on a time basis.
Earned value is one of the most useful project cost management techniques, and you can learn more about it here.
Project cost management software
As you can probably gather form this article alone, project cost management is an extensive and potentially messy part of overall project management.
Because of all of the moving pieces and documents behind project cost management, it is one of the best parts of your business which can be handled more efficiently through software.
There are many different project cost management solutions on the market, some which are designed specifically for cost estimating or budgeting, and others which are designed for project cost control and implementing strong document and process governance.
For most companies, the relatively rigid and slow processes of project cost management planning and estimating is done quite well, but the wheels quickly fall off when it comes to project delivery.
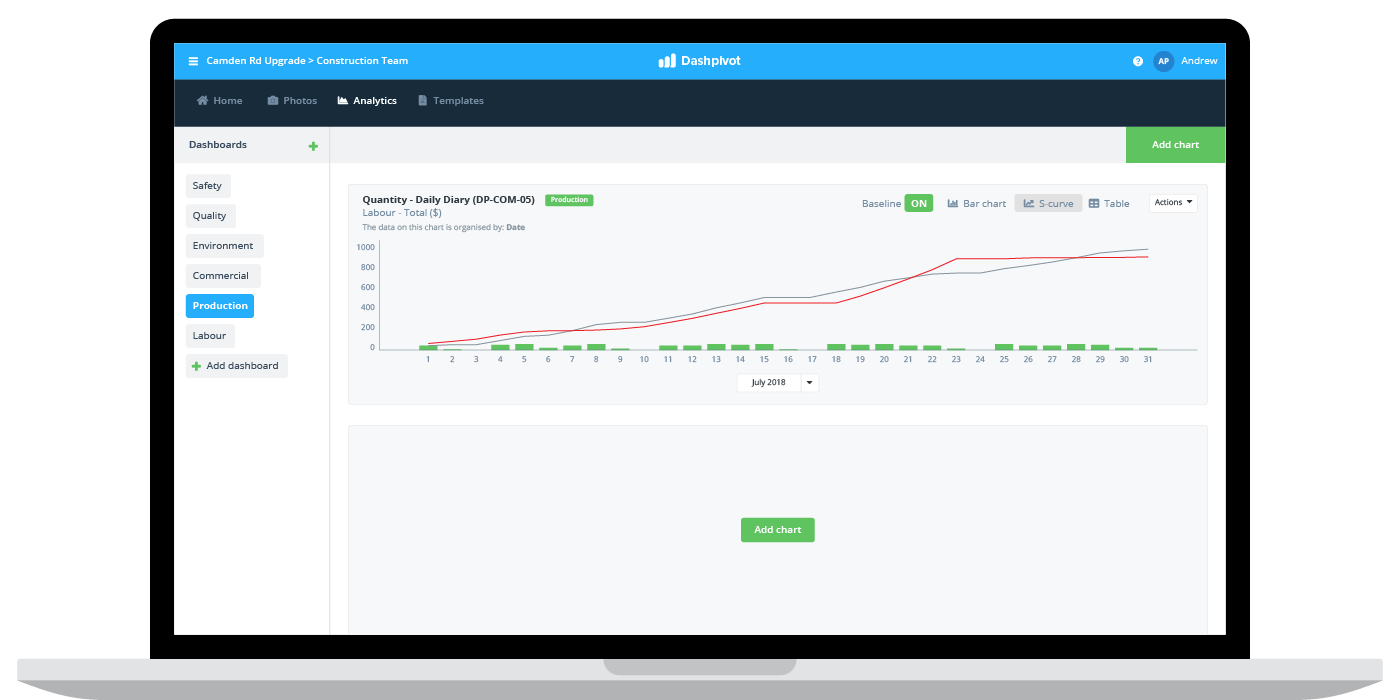
Looking for project delivery systems like Dashpivot, which can build smart financial, production and quality decisions into your every day procedures is critical to creating reliable project cost management processes across every stage of project delivery.
Tips for sticking to the cost plan and managing project costs more effectively
Project cost management is easier said than done, and keeping a project on time and on budget can be hard work.
Many companies and project managers create contingency plans and pad certain parts of a project to mitigate against shocks and forces, but many don't create enough margin.
The planning fallacy often pushes us towards being optimistic about our projects (and maybe slightly delusional) and moves us away from looking to previous fails, shortfalls and historical data.
Here are some tips which are applicable to most project-based companies which can help companies to avoid big misses and poor project cost management failures:
Account for natural disasters and events - Creating padding and margin for significant major events such as natural disasters, especially if the location is prone to a specific type of event, is a great way to protect a company and project. Many things during the course of a project can be outside of your control, but planning for them brings the project cost management back under your control.
Account for 'unexpected' costs - Most project-based companies are focused on delivering projects and allocating cost towards their normal operations, but there are many expected costs associated with managing a business including legal and administrative costs.
Track everything in real-time - The decisions companies and project managers make during the course of a project is often only as good as the data at their fingertips, and one aspect of good data is it's recency - especially when gauging performance on a cost management basis.
Enterprise content management softwares and other cloud-based tools like we looked at above have made tracking projects in real-time relatively easy today. Workers can document progress on site, and all of this data can be fed straight into an information management system - in contrast to the past where everything was done manually.
Make good decisions quickly - Many companies fail to respond quickly enough to the project cost management data they do have, and many decisions and a lot of information moves slowly. Speeding up decision making through smarter collaborative tools and procedures is an easy way to ensure all of your decisions are made and executed more smoothly.
These tips are only the 'tip' of the project cost management iceberg, and there are many other foundational steps which a company must make - many of them referenced above - to enable good and reliable project cost management.
There are many aspects of every project which are important including quality and safety, but the one thing which often separates a successful project from a failed one is how much it cost - and how well those costs were managed throughout the project.
People in 100+ countries use this software to do better project cost management from start to finish.